SRADHO: statistical reduction approach with deep hyper optimization for disease classification using artificial intelligence
- PMID: 39774278
- PMCID: PMC11707201
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82838-1
SRADHO: statistical reduction approach with deep hyper optimization for disease classification using artificial intelligence
Abstract
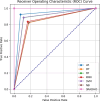
Artificial Intelligence techniques are being used to analyse vast amounts of medical data and assist in the accurate and early diagnosis of diseases. The common brain related diseases are faced by most of the people which affects the structure and function of the brain. Artificial neural networks have been extensively used for disease prediction and diagnosis due to their ability to learn complex patterns and relationships from large datasets. However, there are some problems like over-fitting, under-fitting, vanishing gradient and increased elapsed time occurred in the course of data analysis and prediction which results in performance degradation of the model. Therefore, a complex structure perception is much essential by avoiding over-fitting and under-fitting. This empirical study presents a statistical reduction approach along with deep hyper optimization (SRADHO) technique for better feature selection and disease classification with reduced elapsed time. Deep hyper optimization combines deep learning models with hyperparameter tuning to automatically identify the most relevant features, optimizing model accuracy and reducing dimensionality. SRADHO is used to calibrate the weight, bias and select the optimal number of hyperparameters in the hidden layer using Bayesian optimization approach. Bayesian optimization uses a probabilistic model to efficiently search the hyperparameter space, identifying configurations that maximize model performance while minimizing the number of evaluations. Three benchmark datasets and the classifier models logistic regression, decision tree, random forest, K-nearest neighbour, support vector machine and Naïve Bayes are used for experimentation. The proposed SRADHO algorithm achieves 98.2% of accuracy, 97.2% of precision rate, 98.3% of recall rate and 98.1% of F1-Score value with 0.3% of error rate. The execution time for SRADHO algorithm is 12 s.
Keywords: Bayesian optimization; Deep hyper optimization; Feature selection; Singular matrix; Statistical reduction approach.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures































References
-
- Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Luo, X. & Zhao, H. Diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease based on SHAP value feature selection. Biocybernet. Biomed. Eng.42, 856–869. 10.1016/j.bbe.2022.06.007 (2022).
-
- Arora, P., Mishra, A. & Malhi, A. Machine learning ensemble for the Parkinson’s disease using protein sequences. Multimed Tools Appl81, 32215–32242. 10.1007/s11042-022-12960-7 (2022).
-
- Shoily, T. I., Islam, T., Jannat, S., Tanna, S. A., Alif, T. M., Ema, R. R., Detection of Stroke Disease using Machine Learning Algorithms. In 2019 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kanpur, India, 2019, pp. 1–6, 10.1109/ICCCNT45670.2019.8944689.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

