Prevalence and quality of life associated with erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39774734
- PMCID: PMC11655038
- DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2024.0045.R1.03072024
Prevalence and quality of life associated with erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Genitourinary health significantly affects the quality of life of men, particularly those in middle age. Recent studies have shown that more than half of the men aged over 40 years experience some degree of low urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) or erectile dysfunction (ED).
Objective: To assess the prevalence of ED and LUTS in middle-aged men and correlate this with quality of life data.
Design and setting: A cross-sectional study was conducted in a municipality in the countryside of São Paulo.
Methods: A trained team collected data between July 2021 and August 2022 through face-to-face interviews using a characterization instrument, International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), International Index of Erectile Function-6 (IIEF-6), and World Health Organization Quality-of-Life Scale.
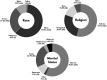
Results: The study included 375 male participants with a median age of 53 years (interquartile range [IQR] 38.5-66). The IIEF-6 showed the presence of some degree of ED in 51.1% (n = 188) of patients, with a median score of 25 (IQR 21-29). The IPSS revealed that 35.2% (n = 132) of the patients had some degree of LUTS, with a median score of 5 (IQR 2-11). The urological questionnaires had a direct proportional correlation with age (P < 0.001) and significant differences between the medians of different marital statuses (P < 0.001). The presence or severity of these disorders was inversely correlated with the individuals' quality of life (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: ED and LUTS significantly correlated with the quality of life, marital status, and age in men.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- Martins F. Saúde do homem: cuidado e prevenção devem ser feitos em todas as fases da vida. Ministério da Saúde; Brasília; 2022: 2022. [Accessed in 2023 (Nov. 10)]. nov. Available from: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/assuntos/noticias/2022/novembro/saude-do-....
-
- Batista JV, Lemos MHS, Silva FM, et al. Perfil epidemiológico da mortalidade masculina no Brasil, 2014-2018. Research, Society and Development. 2021;10(5):e51710515248. doi: 10.33448/rsd-v10i5.15248. - DOI
-
- Figueredo S, Coelho C, Alves De Melo R. Assistência ao Homem na Estratégia Saúde da Família Assistance to the Man in the Family Health Strategy. Id on Line Rev Mult Psic. 2018;12(41):485–508. doi: 10.14295/idonline.v12i41.1231. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical