Mitotic block and epigenetic repression underlie neurodevelopmental defects and neurobehavioral deficits in congenital heart disease
- PMID: 39774941
- PMCID: PMC11707140
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55741-6
Mitotic block and epigenetic repression underlie neurodevelopmental defects and neurobehavioral deficits in congenital heart disease
Abstract
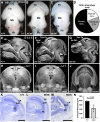
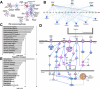
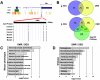
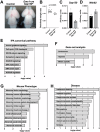
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a severe congenital heart disease associated with microcephaly and poor neurodevelopmental outcomes. Here we show that the Ohia HLHS mouse model, with mutations in Sap130, a chromatin modifier, and Pcdha9, a cell adhesion protein, also exhibits microcephaly associated with mitotic block and increased apoptosis leading to impaired cortical neurogenesis. Transcriptome profiling, DNA methylation, and Sap130 ChIPseq analyses all demonstrate dysregulation of genes associated with autism and cognitive impairment. This includes perturbation of REST transcriptional regulation of neurogenesis, disruption of CREB signaling regulating synaptic plasticity, and defects in neurovascular coupling mediating cerebral blood flow. Adult mice harboring either the Pcdha9 mutation, which show normal brain anatomy, or forebrain-specific Sap130 deletion via Emx1-Cre, which show microcephaly, both demonstrate learning and memory deficits and autism-like behavior. These findings provide mechanistic insights indicating the adverse neurodevelopment in HLHS may involve cell autonomous/nonautonomous defects and epigenetic dysregulation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Update of
-
Mitotic Block and Epigenetic Repression Underlie Neurodevelopmental Defects and Neurobehavioral Deficits in Congenital Heart Disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 26:2023.11.05.565716. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.05.565716. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 7;16(1):469. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55741-6. PMID: 38464057 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hoffman, J. I. & Kaplan, S. The incidence of congenital heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.39, 1890–1900 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Marino, B. S. et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with congenital heart disease: evaluation and management: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation126, 1143–1172 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21 EB023507/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HD097967/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS121706/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 847524/American Heart Association (American Heart Association, Inc.)
- HL14278/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

