Hybrid Prairie Dog and Dwarf Mongoose optimization algorithm-based application placement and resource scheduling technique for fog computing environment
- PMID: 39774989
- PMCID: PMC11707010
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-85142-8
Hybrid Prairie Dog and Dwarf Mongoose optimization algorithm-based application placement and resource scheduling technique for fog computing environment
Abstract
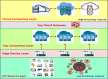
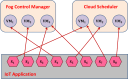
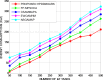
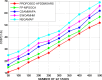
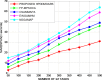
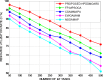
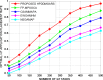
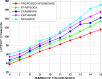
The fog computing paradigm is better for creating delay-sensitive applications in Internet of Things (IoT). As the fog devices are resource constrained, the deployment of diversified IoT applications requires effective ways for determining available resources. Therefore, implementing an efficient resource management strategy is the optimal choice for satisfying application Quality of Service (QoS) requirements to preserve the system performance. Developing an effective resource management system with many QoS criteria is a non-deterministic polynomial time (NP) complete problem. The study applies the Hybrid Prairie Dog and Dwarf Mongoose Optimisation Algorithm-based Resource Scheduling (HPDDMOARS) Technique to effectively position IoT applications and meet fog computing QoS criteria. This HPDDMOARS technique is formulated as a weighted multi-objective IoT application placement mechanism which targets optimizing the three main parameters that considered energy, cost and makespan into account. It employed Prairie Dog Optimization Algorithm (PDOA) for exploring the possibility that helps in mapping the IoT services to the available computing services in fog computing scenario. It also derived the significance of Dwarf Mongoose Optimization Algorithm (DMOA) which helps in exploiting the local factors that helped in satisfying at least one objective of QoS index. It hybridized the benefits of PDOA and DMOA mutually for the objective of balancing the phases of exploration and exploitation such that potential mapping between the IoT tasks and the available computational resources can be achieved in the fog computing environment. The experimental validation of the proposed HPDDMOARS achieved with different number of IoT applications confirmed minimized energy consumptions of 22.18%, reduced makespan of 24.98%, and lowered cost of 18.64% than the baseline metaheuristic application deployment approaches.
Keywords: Dwarf Mongoose optimization algorithm (DMOA); Fog computing; Internet of things (IoT); Prairie Dog optimization algorithm (PDOA); Resource scheduling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures




References
-
- Zolghadri, M., Asghari, P., Dashti, S. E. & Hedayati, A. Resource allocation in fog–cloud environments: state of the art. J. Netw. Comput. Appl.227, 103891 (2024). - DOI
-
- Ntumba, P., Georgantas, N. & Christophides, V. Adaptive scheduling of continuous operators for IoT Edge analytics. Future Generation Comput. Syst.158, 277–293 (2024). - DOI
-
- Lin, S. et al. Cocv: a compression algorithm for time-series data with continuous constant values in IoT-based monitoring systems. Internet Things. 25, 101049 (2024). - DOI
-
- Apat, H. K., Sahoo, B., Goswami, V. & Barik, R. K. A hybrid meta-heuristic algorithm for multi-objective IoT service placement in fog computing environments. Decis. Analytics J.10, 100379 (2024). - DOI
-
- Devi, N. et al. A systematic literature review for load balancing and task scheduling techniques in cloud computing. Artif. Intell. Rev.57(10), 276 (2024). - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

