A machine learning approach for estimating Eastern Asian origins from massive screening of Y chromosomal short tandem repeats polymorphisms
- PMID: 39775035
- PMCID: PMC11850560
- DOI: 10.1007/s00414-024-03406-w
A machine learning approach for estimating Eastern Asian origins from massive screening of Y chromosomal short tandem repeats polymorphisms
Abstract
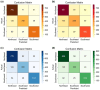
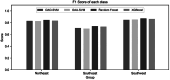
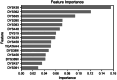
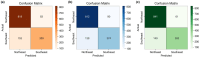
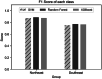
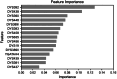
Inferring the ancestral origin of DNA evidence recovered from crime scenes is crucial in forensic investigations, especially in the absence of a direct suspect match. Ancestry informative markers (AIMs) have been widely researched and commercially developed into panels targeting multiple continental regions. However, existing forensic ancestry inference panels typically group East Asian individuals into a homogenous category without further differentiation. In this study, we screened Y chromosomal short tandem repeat (Y-STR) haplotypes from 10,154 Asian individuals to explore their genetic structure and generate an ancestry inference tool through a machine learning (ML) approach. Our research identified distinct genetic separations between East Asians and their neighboring Southwest Asians, with tendencies of northern and southern differentiation observed within East Asian populations. All machine learning models developed in this study demonstrated high accuracy, with the Asian classification model achieving an optimal performance of 82.92% and the East Asian classification model reaching 84.98% accuracy. This work not only deepens the understanding of genetic substructures within Asian populations but also showcases the potential of ML in forensic ancestry inference using extensive Y-STR data. By employing computational methods to analyze intricate genetic datasets, we can enhance the resolution of ancestry in forensic contexts involving Asian populations.
Keywords: Biogeographical origin; East Asia; Machine learning; Short tandem repeat; Y chromosome.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: Approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute (IRB No. 1404-068-572). The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent to participate: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Competing interests: The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Li CX, Pakstis AJ, Jiang L, Wei YL, Sun QF, Wu H, Bulbul O, Wang P, Kang LL, Kidd JR, Kidd KK (2016) A panel of 74 AISNPs: Improved ancestry inference within Eastern Asia. Forensic Sci International: Genet 23:101–110. 10.1016/j.fsigen.2016.04.002 - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Zhu Q, Huang Y, Li X, Wei Y, Wang H, Zhang J (2022) An efficient ancestry informative SNPs panel for further discriminating east Asian populations. Electrophoresis 43:1774–1783. 10.1002/elps.202100349 - PubMed
-
- Sun K, Yao Y, Yun L, Zhang C, Xie J, Qian X, Tang Q, Sun L (2022) Application of machine learning for ancestry inference using multi-InDel markers. Forensic Sci International: Genet 59:102702. 10.1016/j.fsigen.2022.102702 - PubMed
-
- Du R, Xiao C, Cavalli-Sforza L (1997) Genetic distances between Chinese populations calculated on gene frequencies of 38 loci. Sci China Ser C: Life Sci 40:613–621. 10.1007/BF02882691 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

