Randomized controlled trial on effect of different routes of dexmedetomidine on Haemodynamics in patients undergoing saphenectomy under epidural anaesthesia
- PMID: 39775100
- PMCID: PMC11706940
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-85299-2
Randomized controlled trial on effect of different routes of dexmedetomidine on Haemodynamics in patients undergoing saphenectomy under epidural anaesthesia
Abstract
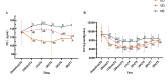
The effect of epidural infusion of dexmedetomidine on haemodynamics is unclear. This study aimed to explore the effects of epidural or intravenous infusion of dexmedetomidine on haemodynamics during lower extremity varicose veins surgery (saphenectomy) under epidural anaesthesia. Ninety patients were randomly allocated to three groups: ED group (epidural: 0.59% ropivacaine plus 0.5 µg/kg dexmedetomidine, intravenous: normal saline), VD group (epidural: 0.59% ropivacaine plus normal saline, intravenous: 0.5 µg/kg dexmedetomidine), or NS group (epidural: 0.59% ropivacaine plus normal saline, intravenous: normal saline). The primary outcome was the systolic blood pressure (SBP) at before anaesthesia (T0) and at 5 (T1), 15 (T2), and 30 min (T3) and 1 (T4), 2 (T5), 4 (T6), 6 (T7), and 8 h (T8) after dexmedetomidine infusion. The secondary outcomes were diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and heart rate (HR) at T0 - 8, plasma norepinephrine (NE), myocardial oxygen consumption (MVO2) and anesthesia efficacy. Adverse reactions and other general data were also recorded. Compared with those in the NS group, the SBP at T3 - 7 and DBP at T4 - 5,7 were significantly lower in the ED group (P = 0.008, 0.001, 0.001, 0.001, 0.038 and P = 0.017, 0.006, 0.044, respectively), and the SBP and DBP at T1 - 8 were lower in the VD group (P < 0.001, 0.001, 0.001, 0.001, 0.004 and P < 0.001, 0.001, 0.001, 0.002, 0.001, 0.001, 0.001, 0.036, respectively). The SBP and DBP at T1 - 2 in the ED group were greater than those in the VD group (P = 0.021, 0.01 and P = 0.001, 0.011, respectively). The HR at T3 - 4,6-7 was lower in the ED group than in the NS group (P < 0.001, 0.021, 0.002, 0.004, respectively). Compared with that in the VD group, the HR in the ED group at T7 was significantly lower (P < 0.001). Anaesthesia efficiency was improved in the ED group compared with VD and NS groups. The incidence of hypotension was lower in the ED group than in the VD group (P = 0.003). The combination of 0.5 µg/kg dexmedetomidine and 0.59% ropivacaine for epidural anaesthesia provides more stable haemodynamics with a lower incidence of hypotension and improved efficiency of epidural anaesthesia in patients undergoing saphenectomy.
Keywords: Administration routes; Anaesthetic effect; Dexmedetomidine; Epidural anaesthesia; Haemodynamics; Ropivacaine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and informed consent: All procedures performed on the patients were in accordance with the tenets of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. This protocol was reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College (Ref. 2022ER073-1). Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal on request.
Figures



References
-
- Wang, W., Ni, B. B., Shen, H. & Lu, H. Local anesthesia, epidural anesthesia and general anesthesia comparison in lumbar disc herniation: a network meta-analysis. Acta Orthop. Belg.88 (4), 661–665. 10.52628/88.4.9922 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Zheng, B. et al. Efficacy and safety of epidural anesthesia versus local anesthesia in percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Palliat. Med.11 (8), 2676–2684. 10.21037/apm-21-3413 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Shui, M., Zhao, D., Xue, Z. & Wu, A. Impact of Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia Versus General Anesthesia on Perioperative Outcomes in patients undergoing lumbar spine surgery: an updated systematic review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Spine Surg.36 (6), 227–236. 10.1097/BSD.0000000000001374 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Pirenne, V., Dewinter, G. & Van de Velde, M. Spinal anaesthesia in obstetrics. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol.37 (2), 101–108. 10.1016/j.bpa.2023.03.006 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Garg, B., Ahuja, K. & Sharan, A. D. Regional Anesthesia for spine surgery. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg.30 (17), 809–819. 10.5435/JAAOS-D-22-00101 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

