Multimodal deep ensemble classification system with wearable vibration sensor for detecting throat-related events
- PMID: 39775108
- PMCID: PMC11706958
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01417-w
Multimodal deep ensemble classification system with wearable vibration sensor for detecting throat-related events
Abstract
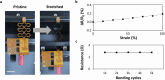
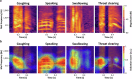
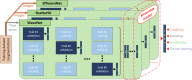
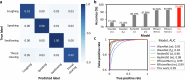
Dysphagia, a swallowing disorder, requires continuous monitoring of throat-related events to obtain comprehensive insights into the patient's pharyngeal and laryngeal functions. However, conventional assessments were performed by medical professionals in clinical settings, limiting persistent monitoring. We demonstrate feasibility of a ubiquitous monitoring system for autonomously detecting throat-related events utilizing a soft skin-attachable throat vibration sensor (STVS). The STVS accurately records throat vibrations without interference from surrounding noise, enabling measurement of subtle sounds such as swallowing. Out of the continuous data stream, we automatically classify events of interest using an ensemble-based deep learning model. The proposed model integrates multiple deep neural networks based on multi-modal acoustic features of throat-related events to enhance robustness and accuracy of classification. The performance of our model outperforms previous studies with a classification accuracy of 95.96%. These results show the potential of wearable solutions for improving dysphagia management and patient outcomes outside of clinical environments.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Wearable System for Monitoring Neurological Disorder Events with Multi-Class Classification Model in Daily Life.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2024 Jul;2024:1-4. doi: 10.1109/EMBC53108.2024.10782047. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2024. PMID: 40039282
-
An ensemble deep-learning approach for single-trial EEG classification of vibration intensity.J Neural Eng. 2023 Sep 29;20(5). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/acfbf9. J Neural Eng. 2023. PMID: 37732958
-
Ensemble neural network approach detecting pain intensity from facial expressions.Artif Intell Med. 2020 Sep;109:101954. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101954. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Artif Intell Med. 2020. PMID: 34756219
-
Ensemble machine learning model trained on a new synthesized dataset generalizes well for stress prediction using wearable devices.J Biomed Inform. 2023 Dec;148:104556. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2023.104556. Epub 2023 Dec 2. J Biomed Inform. 2023. PMID: 38048895
-
Automatic Clinical Assessment of Swallowing Behavior and Diagnosis of Silent Aspiration Using Wireless Multimodal Wearable Electronics.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(34):e2404211. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404211. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38981027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clavé, P. & Shaker, R. Dysphagia: current reality and scope of the problem. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.12, 259–270 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Sungsinchai, S., Niamnuy, C., Wattanapan, P., Charoenchaitrakool, M. & Devahastin, S. Texture modification technologies and their opportunities for the production of dysphagia foods: a review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf.18, 1898–1912 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Labeit, B. et al. The assessment of dysphagia after stroke: state of the art and future directions. Lancet Neurol.22, 858–870 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Rommel, N. & Hamdy, S. Oropharyngeal dysphagia: manifestations and diagnosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.13, 49–59 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Murry, T., Carrau, R. L. & Chan, K. Clinical Management of Swallowing Disorders (Plural Publishing, 2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

