Exosomal NEDD4L derived from HG+oxLDL-induced vascular endothelial cells accelerates macrophage M1 polarization and oxLDL uptake by ubiquitinating IκBα and PPARγ
- PMID: 39775116
- PMCID: PMC11706887
- DOI: 10.1007/s10565-024-09973-3
Exosomal NEDD4L derived from HG+oxLDL-induced vascular endothelial cells accelerates macrophage M1 polarization and oxLDL uptake by ubiquitinating IκBα and PPARγ
Abstract
Background: Vascular endothelial cell-derived exosomes are thought to mediate disease progression by regulating macrophage polarization. However, its mechanism in diabetes mellitus (DM)-related atherosclerosis (AS) progress is unclear.
Methods: High-glucose (HG) and oxLDL were used to induce human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (HCMECs) to mimic DM-related AS model. The conditioned medium (CM) from HG+oxLDL-induced HCMECs was incubated with THP1-M0 monocytes treated with LPS or oxLDL. The mRNA levels of macrophage M1/M2 polarization markers, NEDD4L, IκBα and PPARγ were determined by qRT-PCR. Flow cytometry was used to analyze macrophage marker. Dil-labeled oxLDL and oil red O staining were performed to assess oxLDL uptake by THP1-M0 cells. The levels of inflammatory factors were examined using ELISA. Transmission electron microscope was used for observing foam cell formation and exosome morphology. The protein levels of p-Smad1/Smad1, p-Smad2/Smad2, p-IκBα/IκBα, p-P65/P65, anti-lipid metabolism-related markers, and NEDD4L were tested by western blot. The interaction between NEDD4L and IκBα or PPARγ was assessed by Co-IP assay.
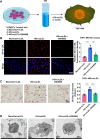
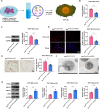
Results: The CM of HG+oxLDL-induced HCMECs could promote macrophage M1 polarization, oxLDL uptake and foam cell formation, and exosome inhibiter GW4869 eliminated these effects. NEDD4L was overexpressed in exosomes from HG+oxLDL-induced HCMECs, which could be taken up by THP1-M0 cells. Exosomal NEDD4L knockdown inhibited macrophage M1 polarization, oxLDL uptake and foam cell formation by reducing the protein levels of p-Smad1/Smad1, p-Smad2/Smad2, p-IκBα/IκBα and p-P65/P65. NEDD4L could reduce IκBα and PPARγ expression through ubiquitination.
Conclusion: HG+oxLDL-induced HCMECs-derived exosomal NEDD4L could enhance the ubiquitination of IκBα and PPARγ to facilitate macrophage M1 polarization and oxLDL uptake, thus accelerating DM-related AS.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Diabetes mellitus; Exosome; Macrophages; NEDD4L.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Bai S, Yin Q, Dong T, Dai F, Qin Y, Ye L, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes ameliorate endothelial dysfunction in a mouse model of diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110756. - PubMed
-
- Cui L, Ma J. NEDD4L Promotes IkappaBalpha Ubiquitination and Degradation in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr Eye Res. 2024;49(1):62–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

