The effects of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway on the in vitro differentiation of rat BMSCs into leydig cells
- PMID: 39775149
- PMCID: PMC11707357
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-85674-z
The effects of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway on the in vitro differentiation of rat BMSCs into leydig cells
Abstract
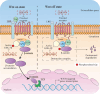
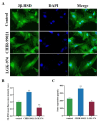
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH) refers to sexual and non-sexual symptoms in men caused by age-related decreases in circulating testosterone. Leydig cells (LCs) transplantation is considered to be one of a viable approach for LOH therapy, but the limited source of LCs limits the application of this approach. The aim of this study was to induce the directed differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) into LCs in vitro, and explore the potential involvement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the differentiation process. BMSCs were extracted from rats and characterized by flow cytometry for positive rates of mesenchymal stem cell markers CD29, CD44, CD90, and the hematopoietic marker CD45. BMSCs were divided into three groups: Control, Wnt agonist (CHIR-99021), and Wnt inhibitor (LGK-974), each incubated for 14 days. ELISA and RT-qPCR were used to verify the protein and mRNA expression of β-catenin, LRP5 and TCF, the key factors in Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The average fluorescence intensity of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD) on the surface of LCs was detected by immunofluorescence (IF) assay. The content of testosterone secreted in cell culture medium was detected by ELISA. The results of flow cytometry indicated that we successfully extracted and cultured BMSCs. Moreover, post 14 days of incubation, the changes of β-catenin, LRP5 and TCF, at the protein and mRNA level demonstrate successful intervention in the activation and inhibition of the intracellular Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Compared with the control group, the LCs surface marker 3β-HSD expression intensity in the CHIR-99,021 group was significantly increased by 69% (p < 0.01), while significantly decreased by 59% in LGK-974 group (p < 0.01). The ELISA results indicated a higher testosterone concentration in the CHIR-99,021 group (359.58 ± 17.46 pg/mL) than in the control (225.31 ± 15.42 pg/mL) and LGK-974 groups (183.67 ± 4.47 pg/mL), and the difference was statistically significant (p < 0.05). This study successfully demonstrates the directed differentiation of BMSCs into LCs under the action of inducers. We verified that the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in this differentiation process. The idea proposed in our study for efficiently inducing differentiation of BMSCs into LC in vitro, may provide a safe and sustainable LC source for developing clinically feasible cell transplantation-based LOH therapies.
Keywords: Bone mesenchymal stem cell; Late-onset hypogonadism; Leydig cell; Testosterone; Wnt/β-catenin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The procedures of this study were approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University (permission no: DW2022023), and conducted according to the ARRIVE guidelines.
Figures


References
-
- Andrew, S. M., Haolin, C., Vassilios, P. & Barry, R. Z. Leydig cell aging and the mechanisms of reduced testosterone synthesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.299(1): (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

