Molecular mechanisms of inverse agonism via κ-opioid receptor-G protein complexes
- PMID: 39775170
- PMCID: PMC12202187
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-024-01812-0
Molecular mechanisms of inverse agonism via κ-opioid receptor-G protein complexes
Abstract
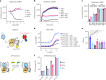
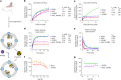
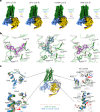
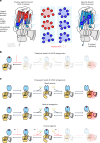
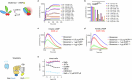
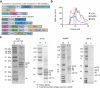
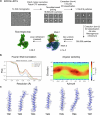
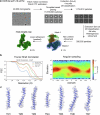
Opioid receptors, a subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), are key therapeutic targets. In the canonical GPCR activation model, agonist binding is required for receptor-G protein complex formation, while antagonists prevent G protein coupling. However, many GPCRs exhibit basal activity, allowing G protein association without an agonist. The pharmacological impact of agonist-free receptor-G protein complexes is poorly understood. Here we present biochemical evidence that certain κ-opioid receptor (KOR) inverse agonists can act via KOR-Gi protein complexes. To investigate this phenomenon, we determined cryo-EM structures of KOR-Gi protein complexes with three inverse agonists: JDTic, norBNI and GB18, corresponding to structures of inverse agonist-bound GPCR-G protein complexes. Remarkably, the orthosteric binding pocket resembles the G protein-free 'inactive' receptor conformation, while the receptor remains coupled to the G protein. In summary, our work challenges the canonical model of receptor antagonism and offers crucial insights into GPCR pharmacology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Chavkin, C., James, I. F. & Goldstein, A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the κ opioid receptor. Science215, 413–415 (1982). - PubMed
-
- Che, T. & Roth, B. L. Structural insights accelerate the discovery of opioid alternatives. Annu. Rev. Biochem.90, 739–761 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Akins, N. S. et al. Alleviation of cocaine withdrawal and pertinent interactions between salvinorin-based antagonists and κ opioid receptor. ACS Chem. Neurosci.14, 958–976 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01DA057790/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- R01 AT012075/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01AT012075/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH)
- R01 DA057790/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM144965/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

