Revealing the impact of tadalafil-loaded proniosomal gel against dexamethasone-delayed wound healing via modulating oxido-inflammatory response and TGF-β/Macrophage activation pathway in rabbit model
- PMID: 39775258
- PMCID: PMC11706462
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315673
Revealing the impact of tadalafil-loaded proniosomal gel against dexamethasone-delayed wound healing via modulating oxido-inflammatory response and TGF-β/Macrophage activation pathway in rabbit model
Abstract
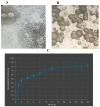
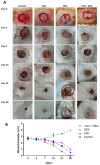
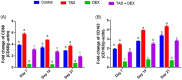
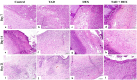
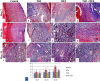
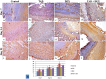
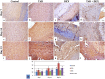
A serious challenge of the chronic administration of dexamethasone (DEX) is a delay in wound healing. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the potential of Tadalafil (TAD)-loaded proniosomal gel to accelerate the healing process of skin wounds in DEX-challenged rabbits. Skin wounds were induced in 48 rabbits of 4 groups (n = 12 per group) and skin wounds were treated by sterile saline (control), TAD-loaded proniosomal gel topically on skin wound, DEX-injected rabbits, and DEX+TAD-loaded proniosomal gel for 4 weeks. The optical photography, transmission electron microscopy, in vitro release profile, and stability studies revealed the successful preparation of the selected formula with good stability. DEX administration was associated with uncontrolled oxido-inflammatory reactions, suppression in immune response in skin wounds, and consequently failure in the healing process. TAD-loaded proniosomal gel-treated rabbits manifested a marked enhancement in the rate of wound closure than control and DEX groups (p < 0.05). The TAD-loaded proniosomal gel successfully antagonized the impacts of DEX by dampening MDA production, and enhancing total antioxidant capacity, coupled with modulation of inflammatory-related genes, inducible nitric oxide synthase, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1β, and matrix metalloproteinase 9, during all healing stages (p < 0.05). This was in combination with significant amplification of immune response-related genes, CD68 and CD163 (p < 0.05). Moreover, the histopathological, Masson's Trichrome-stain, and immune-histochemical studies indicated a successful tissue recovery with the formation of new blood vessels in groups treated with TAD-loaded proniosomal gel, as manifested by well-organized collagen fibers, upregulation of transforming growth factor β1, and vascular endothelial growth factor immune expression in skin tissues (p < 0.05). Overall, the topical application of TAD-loaded proniosomal gel is useful in improving the delayed wound healing linked to DEX therapy via regulating the release of inflammatory/macrophage activation mediators and enhanced antioxidant capacity, angiogenesis, and vascularity.
Copyright: © 2025 Helmy et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong DG, Meyr AJ, Sanfey H, Eidt JF, Mills JL, Billings JA. Basic principles of wound management. Atlas Small Anim Wound Manag Reconstr Surgery; John Wiley Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA. 2018; 33–52.
-
- Rajendran NK, Kumar SSD, Houreld NN, Abrahamse H. A review on nanoparticle based treatment for wound healing. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2018;44: 421–430.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

