Artificial intelligence applied to bed regulation in Rio Grande do Norte: Data analysis and application of machine learning on the "RegulaRN Leitos Gerais" platform
- PMID: 39775276
- PMCID: PMC11684685
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315379
Artificial intelligence applied to bed regulation in Rio Grande do Norte: Data analysis and application of machine learning on the "RegulaRN Leitos Gerais" platform
Abstract
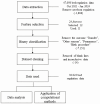
Bed regulation within Brazil's National Health System (SUS) plays a crucial role in managing care for patients in need of hospitalization. In Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil, the RegulaRN Leitos Gerais platform was the information system developed to register requests for bed regulation for COVID-19 cases. However, the platform was expanded to cover a range of diseases that require hospitalization. This study explored different machine learning models in the RegulaRN database, from October 2021 to January 2024, totaling 47,056 regulations. From the data obtained, 12 features were selected from the 24 available. After that, blank and inconclusive data were removed, as well as the outcomes that had values other than discharge and death, rendering a binary classification. Data was also correlated, balanced, and divided into training and test portions for application in machine learning models. The results showed better accuracy (87.77%) and recall (87.77%) for the XGBoost model, and higher precision (87.85%) and F1-Score (87.56%) for the Random Forest and Gradient Boosting models, respectively. As for Specificity (82.94%) and ROC-AUC (82.13%), the Multilayer Perceptron with SGD optimizer obtained the highest scores. The results evidenced which models could adequately assist medical regulators during the decision-making process for bed regulation, enabling even more effective regulation and, consequently, greater availability of beds and a decrease in waiting time for patients.
Copyright: © 2024 Barreto et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Barreto TdO, Veras NVR, Cardoso PH, Fernandes FRdS, Medeiros LPdS, Bezerra MV, et al.. Artificial intelligence applied to analyzes during the pandemic: COVID-19 beds occupancy in the state of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence. 2023;6:1290022. doi: 10.3389/frai.2023.1290022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brasil. Portaria nº 1.559, de 1º de agosto de 2008. Institui a Política Nacional de Regulação do Sistema Único de Saúde-SUS. Diário Oficial da União. 2008;.
-
- Brasil. Portaria nº 2, de 28º de setembro de 2017. Consolidação das normas sobre as políticas nacionais de Saú do Sistema Único de Saúde-SUS. Diário Oficial da União. 2017;.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

