Essential tremor with tau pathology features seeds indistinguishable in conformation from Alzheimer's disease and primary age-related tauopathy
- PMID: 39775287
- PMCID: PMC11711841
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-024-02843-6
Essential tremor with tau pathology features seeds indistinguishable in conformation from Alzheimer's disease and primary age-related tauopathy
Abstract
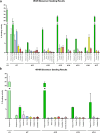
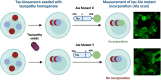
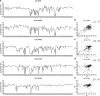
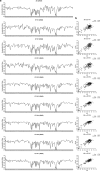
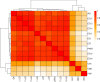
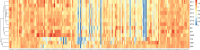
Neurodegenerative tauopathies are characterized by the deposition of distinct fibrillar tau assemblies, whose rigid core structures correlate with defined neuropathological phenotypes. Essential tremor (ET) is a progressive neurological disorder that, in some cases, is associated with cognitive impairment and tau accumulation. In this study, we explored tau assembly conformation in ET patients with tau pathology using cytometry-based tau biosensor assays. These assays quantify the tau seeding activity present in brain homogenates by detecting the conversion of intracellular tau-fluorescent protein fusions from a soluble to an aggregated state. Pathogenic tau assemblies exhibit seeding barriers, where a specific assembly structure cannot serve as a template for a native monomer if the amino acid sequences are incompatible. We recently leveraged this species barrier to define tauopathies systematically by substituting alanine (Ala) into the tau monomer and measuring its incorporation into seeded aggregates within biosensor cells. This Ala scan precisely classified the conformation of tau seeds from various tauopathies. In this study, we analyzed 18 ET patient brains with tau pathology, detecting robust tau seeding activity in 9 (50%) of the cases, predominantly localized to the temporal pole and temporal cortex. We further examined 8 of these ET cases using the Ala scan and found that the amino acid requirements for tau monomer incorporation into aggregates seeded from ET brain homogenates were identical to those of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and primary age-related tauopathy (PART), and distinct from other tauopathies, such as corticobasal degeneration (CBD), chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). These findings indicate that in a pathologically confined subset of ET cases with significant tau pathology, tau assembly cores are identical to those seen in AD and PART. This could facilitate more precise diagnosis and targeted therapies for ET patients presenting with cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Alanine scan; Alzheimer’s disease; Essential tremor; PART; Tau.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Essential tremor with tau pathology features seeds indistinguishable in conformation from Alzheimer's disease and primary age-related tauopathy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 20:2024.10.12.617973. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.12.617973. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Acta Neuropathol. 2025 Jan 8;149(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02843-6. PMID: 39464029 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Louis ED, Martuscello RT, Gionco JT, Hartstone WG, Musacchio JB, Portenti M et al (2023) Histopathology of the cerebellar cortex in essential tremor and other neurodegenerative motor disorders: comparative analysis of 320 brains. Acta Neuropathol 145:265–283. 10.1007/s00401-022-02535-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

