The relationship between physical education teachers' competence support and middle school students' participation in sports: A chain mediation model of perceived competence and exercise persistence
- PMID: 39775358
- PMCID: PMC11706385
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314338
The relationship between physical education teachers' competence support and middle school students' participation in sports: A chain mediation model of perceived competence and exercise persistence
Abstract
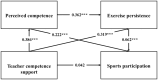
This study explores the relationship between physical education teachers' support and middle school students' participation in sports. It also clarifies this relationship's mediating roles of perceived competence and exercise persistence. A questionnaire survey involved 879 Chinese middle school students, consisting of 434 males and 445 females. The results indicate a significant positive correlation between teachers' competence support and students' participation in sports (p < 0.01). Perceived competence and exercise persistence as important mediators between teachers' competence support and students' involvement in sports, with the mediation effect comprising independent mediation by perceived competence and exercise persistence and a chain mediation effect involving both. The effect value was 0.156, with contributions of 60.4%, 43.6%, and 73.1% to the total mediating effect, respectively. In physical education courses, teachers should enhance their competence to support students, increase students' interest in learning, and promote the development of sports participation. By understanding the predictive roles of teacher support, perceived competence, and exercise persistence on sports participation, strategies can be developed to better enhance students' levels of participation in physical activities, thereby improving their beliefs about physical health and their confidence in exercising.
Copyright: © 2025 Liu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global status report on physical activity 2022: country profiles: World Health Organization; 2022.
-
- Eberline A, Judge L, Walsh A, Hensley L. Relationship of Enjoyment, Perceived Competence, and Cardiorespiratory Fitness to Physical Activity Levels of Elementary School Children. The Physical Educator. 2018;75:394–413. doi: 10.18666/TPE-2018-V75-I3-8161 - DOI
-
- Ghorbani S, Noohpisheh S, Shakki M. Gender Differences in the Relationship between Perceived Competence and Physical Activity in Middle School Students: Mediating Role of Enjoyment. International Journal of School Health. 2020:14–20. doi: 10.30476/intjsh.2020.85668.1056 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical