Identification and characterisation of temporal abundance of microRNAs in synovial fluid from an experimental equine model of osteoarthritis
- PMID: 39775906
- PMCID: PMC12135755
- DOI: 10.1111/evj.14456
Identification and characterisation of temporal abundance of microRNAs in synovial fluid from an experimental equine model of osteoarthritis
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs, a class of small noncoding RNAs, serve as post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression and are present in a stable and quantifiable form in biological fluids. MicroRNAs may influence intra-articular responses and the course of disease, but very little is known about their temporal changes in osteoarthritis.
Objectives: To identify miRNAs and characterise the temporal changes in their abundance in SF from horses with experimentally induced osteoarthritis. We hypothesised that the abundance of miRNA would change during disease progression.
Study design: In vivo experiments.
Methods: RNA extracted from synovial fluid obtained sequentially (Day 0, 28 and 70) from nine horses with experimentally induced osteoarthritis was subjected to small RNA sequencing using the Illumina Hiseq 4000 sequencing platform. Differentially abundant miRNAs underwent further validation and mapping of temporal abundance (Day 0, 14, 17, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63 and 70 days after osteoarthritis induction) by microfluidic reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR. Bioinformatic analyses were performed to predict potential biological associations and target genes of the differentially abundant microRNAs.
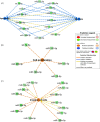
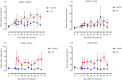
Results: Small RNA sequencing revealed 61 differentially abundant microRNAs at an early osteoarthritis stage (Day 28), and subsequent reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR analysis validated 20 of these. Significant biological functions of the differentially abundant microRNAs were apoptosis, necrosis, cell proliferation and cell invasion. Following validation, four microRNAs (miRNA-199b-3p, miRNA-139-5p, miRNA-1839 and miRNA-151-5p) were detected in more than 50% of the synovial fluid samples and had higher abundance in osteoarthritic than in control joints.
Main limitations: Limited sample size.
Conclusion: This is the first study to determine longitudinal changes in synovial fluid microRNA abundance in an equine model of osteoarthritis. Larger studies are needed in naturally occurring osteoarthritis to interrogate putative changes identified by this study.
Keywords: horse; microRNA; osteoarthritis; post‐transcriptional gene regulation; reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction; small RNA sequencing; synovial fluid.
© 2025 The Author(s). Equine Veterinary Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of EVJ Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- De Guire V, Robitaille R, Tetreault N, Guerin R, Menard C, Bambace N, et al. Circulating miRNAs as sensitive and specific biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of human diseases: promises and challenges. Clin Biochem. 2013;46(10–11):846–860. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

