Exploration of preschool hearing screening at primary healthcare centers in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39776543
- PMCID: PMC11701338
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2024.10.001
Exploration of preschool hearing screening at primary healthcare centers in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
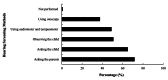
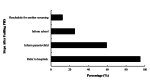
The hearing status of children should be examined throughout early childhood, even if they have passed the newborn hearing loss because hearing loss can occur at any time and may affect their ability to learn. Preschool hearing screening (PHS) is vital to continue screening throughout early childhood. The current practice of PHS in the primary healthcare centers (PHCs) in Saudi Arabia is unknown. The purpose of this study was to investigate PHS in the PHCs. This cross-sectional descriptive study used an in-person-administered questionnaire to collect data. A total of 106 out of 120 participants (male = 61; female = 45) representing the PHCs in Riyadh were interviewed. Most of the participants were aged 31-40 years and held a bachelor's degree as the highest academic qualification with limited years of experience. PHS was mostly performed through subjective measures by asking the parents (71.7%) and the child (65.1%). The audiometric evaluation was conducted for preschool children in only half of the PHCs. General practitioners and nurses usually perform PHS. Substantial gaps in the practice of PHS were identified. The lack of training and appropriate instruments and the need for audiological services were the main challenges. Incorporating robust and objective protocols for PHS into the educational system is a valuable strategy for identifying hearing loss early and reducing its impact through the establishment of effective intervention plans.
Keywords: Audiology; Hearing loss; Preschool children; Primary healthcare center; Saudi Arabia; Screening.
© [copyright 2024] PLA General Hospital Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Production and hosting by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
School-based hearing screening of first-grade students in Saudi Arabia: A pilot study.S Afr J Commun Disord. 2024 Nov 29;71(1):e1-e7. doi: 10.4102/sajcd.v71i1.1063. S Afr J Commun Disord. 2024. PMID: 39625087 Free PMC article.
-
Deaf or hard of hearing children in Saudi Arabia: Status of early intervention services.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jul;86:142-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 27260597
-
Parental knowledge and attitudes to childhood hearing loss and hearing services in Qassim, Saudi Arabia.BMC Pediatr. 2020 Apr 20;20(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-02080-2. BMC Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32312244 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitude and management of hearing screening in children among family physicians in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 31;16(8):e0256647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256647. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34464417 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges of Newborn Hearing Screening Programs in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review.Audiol Res. 2025 Mar 25;15(2):34. doi: 10.3390/audiolres15020034. Audiol Res. 2025. PMID: 40277579 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al Saffer Q., Al-Ghaith T., Alshehri A., Al-Mohammed R., Al Homidi S., Hamza M.M., Herbst C.H., Alazemi N. The capacity of primary health care facilities in Saudi Arabia: infrastructure, services, drug availability, and human resources. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2021;21(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06355-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Abdiljawad K.A. Hearing screening of primary school children. Saudi J. Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;9(2):50–52. doi: 10.4103/1319-8491.275442. - DOI
-
- Al-Mazrou Y.Y. Primary health care in Saudi Arabia: its development and future prospectives. J. Fam. Com. Med. 2002;9(2):15–16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3430179/ - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

