Breaking the silence - systematic review of the socio-cultural underpinnings of men's sexual and reproductive health in Middle East and North Africa (MENA): A handful of taboos?
- PMID: 39776553
- PMCID: PMC11703040
- DOI: 10.1080/20905998.2024.2387511
Breaking the silence - systematic review of the socio-cultural underpinnings of men's sexual and reproductive health in Middle East and North Africa (MENA): A handful of taboos?
Abstract
Background: Sociocultural aspects can impact sexual and reproductive health (SRH). Despite this, no study appraised the socio-cultural underpinnings impacting men's SRH in MENA (Middle East and North Africa). The current systematic review undertook this task.
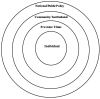
Methods: We searched PubMed and Scopus electronic databases for original articles on socio-cultural aspects of men's SRH published from MENA. Data were extracted from the selected articles and mapped out employing McLeroy's socioecological model. Analyses and data synthesis identified the factors impacting men's experiences of and access to SRH.
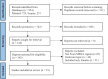
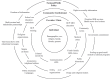
Results: A total of 53 articles were included. Five related socio-cultural underpinnings intertwined with taboos were observed that affect three main SRH topics, HIV, reproduction and sexuality across three broad population groups: HCP/health services, school/university students, and the general public/patients. These underpinnings included 1) Challenges to gender equality; 2) Religious prohibitions and misinterpretations; 3) Sexual rights and taboos; 4) Masculinity and manhood ideals; and 5) Large families and consanguinity. In terms of research, a paradox exists, as we found virtually no research on four socio-cultural underpinnings of men's SRH in MENA pertaining to: a) other STI, despite being common; b) other features of reproduction, despite that religio-cultural factors play a critical role; c) sexuality, despite the high prevalence of sexual disorders, and, d) gender-based violence, despite the widespread partner violence.
Conclusions: Socio-cultural underpinnings are deeply rooted across MENA population groups including HCPs, students, general public, and patients with negative impact on the perceptions and dealings pertaining to men's SRH issues including HIV, reproduction and sexuality. The findings call for concerted widespread efforts to enhance the socio-cultural acceptance of these population groups while highlighting any misinterpretations of religious rules pertaining to men's SRH. Moreover, breaking the silence on such issues necessitates more enthusiasm across MENA health systems, with future research examining the effects of such efforts on the socio-cultural aspects of men's SRH in MENA.
Keywords: MENA; Sexual; culture; religion; reproductive health.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- UNFPA (United Nations Fund for Population Activities) Arab States . Sexual and reproductive health. 2022. [cited 2023 Jul 21]. Available from: https://arabstates.unfpa.org/en/topics/sexualandreproductivehealth
-
- The World Bank . Population, male (% of total population) - Middle East & North Africa. (WA): The World Bank; 2022. [cited 2023 Jul 20]. Available from: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL.MA.ZS?locations=ZQ
-
- OECD iLibrary . Youth at the centre of government action: a review of the Middle East and North Africa. 2023. [cited 2023 Jul 20]. Available from: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/sites/3ced02bf-en/index.html?itemId=/conte...)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
