Cross-modal contrastive learning for unified placenta analysis using photographs
- PMID: 39776848
- PMCID: PMC11701861
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patter.2024.101097
Cross-modal contrastive learning for unified placenta analysis using photographs
Abstract
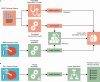
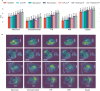
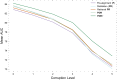
The placenta is vital to maternal and child health but often overlooked in pregnancy studies. Addressing the need for a more accessible and cost-effective method of placental assessment, our study introduces a computational tool designed for the analysis of placental photographs. Leveraging images and pathology reports collected from sites in the United States and Uganda over a 12-year period, we developed a cross-modal contrastive learning algorithm consisting of pre-alignment, distillation, and retrieval modules. Moreover, the proposed robustness evaluation protocol enables statistical assessment of performance improvements, provides deeper insight into the impact of different features on predictions, and offers practical guidance for its application in a variety of settings. Through extensive experimentation, our tool demonstrates an average area under the receiver operating characteristic curve score of over 82% in both internal and external validations, which underscores the potential of our tool to enhance clinical care across diverse environments.
Keywords: contrastive learning; cross-modal; knowledge distillation; placenta analysis; vision and language.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.Z.W., A.D.G., and J.A.G. are named inventors on US patent 11,244,450, “Systems and Methods Utilizing Artificial Intelligence for Placental Assessment and Examination.” It is assigned to The Penn State Research Foundation and Northwestern University. These interests do not influence the integrity of the research, and all efforts have been made to ensure that the research was conducted and presented in an unbiased manner.
Figures






References
-
- Fitzgerald E., Shen M., Yong H.E.J., Wang Z., Pokhvisneva I., Patel S., O’Toole N., Chan S.-Y., Chong Y.S., Chen H., et al. Hofbauer cell function in the term placenta associates with adult cardiovascular and depressive outcomes. Nat. Commun. 2023;14:7120. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42300-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reis A.S., Barboza R., Murillo O., Barateiro A., Peixoto E.P.M., Lima F.A., Gomes V.M., Dombrowski J.G., Leal V.N.C., Araujo F., et al. Inflammasome activation and IL-1 signaling during placental malaria induce poor pregnancy outcomes. Sci. Adv. 2020;6 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax6346. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

