Clinical exome next‑generation sequencing panel for hereditary pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma diagnosis
- PMID: 39776888
- PMCID: PMC11705218
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2024.12784
Clinical exome next‑generation sequencing panel for hereditary pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma diagnosis
Abstract
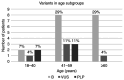
Pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas (PPGLs) are rare neuroendocrine tumors with an annual incidence of ~2 cases per million worldwide. The hereditary form is more likely to present in younger patients. To date, PPGL is considered a complex pathology that is difficult to diagnose. The present study aimed to improve the molecular diagnosis and other driver mutations related to PPGLs using TruSight One clinical exome panel (Illumina, Inc.). The clinical protocol used involved examining 28 patients with suspicion of genetic alterations as the cause of PPGLs. The variants of genes commonly associated with PPGLs (RET, FH, VHL, SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD, NF1, MAX, HIF2A, TMEM127 and TP53) were filtered across the panel. The libraries were sequenced on a MiSeq instrument (Illumina, Inc.) and the result was ≥20X coverage on 95% of the target regions in the panel, calculated by averaging the mean coverage for each exon. The results of sequencing detected 7% of pathogenic variants in the 18-40 years age subgroup and 11% in the 41-59 years age subgroup, whereas no pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants were identified in patients ≥60 years old. The identification of a germline mutation in patients with apparently sporadic PPGLs could lead to an early diagnosis of multiple or more aggressive tumors, or other neoplastic syndromes, in patients. Furthermore, this information may improve the development of targeted primary and secondary prevention programs tailored to these high-risk groups.
Keywords: clinical exome panel; hereditary cancer; next-generation sequencing; paraganglioma; pheochromocytoma.
Copyright: © 2024 Melli et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lloyd RV, Osamura RY, Klöppel G, Rosai J. WHO classification of tumours of endocrine organs. Lloyd RV, Osamura RY, Klöppel G and Rosai J (eds). International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous