Novel rhesus macaque immunoglobulin germline genes identified by three sequencing approaches
- PMID: 39776901
- PMCID: PMC11703713
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1506348
Novel rhesus macaque immunoglobulin germline genes identified by three sequencing approaches
Abstract
Introduction: Rhesus macaques have long been a focus of research for understanding immune responses to human pathogens due to their close phylogenetic relationship with humans. As rhesus macaque antibody germlines show high degrees of polymorphism, the spectrum of database-covered genes expressed in individual macaques remains to be determined.
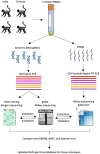
Methods: Here, four rhesus macaques infected with SHIVSF162P3N became a study of interest because they developed broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1. To identify the immunoglobulin heavy chain V-gene (IGHV) germlines in these macaques, we applied three sequencing approaches - genomic DNA (gDNA) TOPO sequencing, gDNA MiSeq, and messenger RNA (mRNA) MiSeq inference with IgDiscover, and illustrated the detection power of each method.
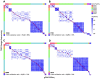
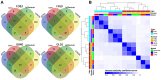
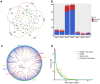
Results: Of the 197 new rhesus IGHV germline sequences identified, 116 (59%) were validated by at least two methods, and 143 (73%) were found in at least two macaques or two sample sources. About 20% of germlines in each macaque are missing from the current database, including a subset frequently expressed. Overall, gDNA MiSeq determined the greatest number of germline sequences, followed by gDNA TOPO sequencing and mRNA MiSeq inference by IgDiscover, with IgDiscover providing direct evidence of allele expression and usage.
Discussion: Our interdisciplinary study sheds light on germline sequencing, enhances the rhesus IGHV germline database, and highlights the importance of germline sequencing in rhesus immune repertoire studies.
Keywords: IGHV genes; NGS; antibody; database; rhesus macaque.
Copyright © 2024 Guo, Waltari, Lu, Sheng and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A primer set for comprehensive amplification of V-genes from rhesus macaque origin based on repertoire sequencing.J Immunol Methods. 2019 Feb;465:67-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2018.11.011. Epub 2018 Nov 22. J Immunol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30471299
-
Development of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies and Their Mapping by Monomeric gp120 in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1-Infected Humans and Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus SHIVSF162P3N-Infected Macaques.J Virol. 2016 Mar 28;90(8):4017-4031. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02898-15. Print 2016 Apr. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26842476 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing IGHV Gene Structural Diversity Enhances Immunoglobulin Repertoire Analysis: Lessons From Rhesus Macaque.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 28;13:818440. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.818440. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35419009 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin VH gene diversity and somatic hypermutation during SIV infection of rhesus macaques.Immunogenetics. 2015 Jul;67(7):355-70. doi: 10.1007/s00251-015-0844-3. Epub 2015 May 21. Immunogenetics. 2015. PMID: 25994147 Free PMC article.
-
Inferred Allelic Variants of Immunoglobulin Receptor Genes: A System for Their Evaluation, Documentation, and Naming.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 18;10:435. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00435. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30936866 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

