Anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody prevents chronic graft-versus-host disease in mice by inducing immune tolerance of CD8+ T cells and alleviating thymus injury
- PMID: 39776911
- PMCID: PMC11703850
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1460687
Anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody prevents chronic graft-versus-host disease in mice by inducing immune tolerance of CD8+ T cells and alleviating thymus injury
Abstract
Background: Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) manifests with characteristics of autoimmune disease with organs attacked by pathogenic helper T cells. Recent studies have highlighted the role of T cells in cGVHD pathogenesis. Due to limited understanding of underlying mechanisms, preventing cGVHD after allogenic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) has become a major challenge.
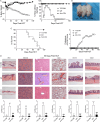
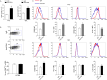
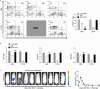
Materials and methods: Here, we used a representative cGVHD model with the donor C57BL/6 to recipient BALB/c combination. Post-HCT, mice were treated with IgG or anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody. The severity of cGVHD was assessed by evaluating symptoms of cGVHD and histopathology examination (H&E) of target organs. Thymus gland damage and defects of the negative selection were assessed by analyzing the CD4+CD8+ double-positive thymocytes, cortical thymic epithelial cells and medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs). Immunotolerance of CD8+ T cells was assessed by detecting the expression of CD80, PD-1, GRAIL and IL-7Rα. Long-term cellular and humoral immunity associated with graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effects were evaluated through detecting the percentage of CD4+ T cells, IgG, IgM and IgA concentrations, and performing tumor challenge experiment.
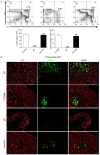
Results: Donor CD8+ T cells caused thymic epithelial cells damage and impaired negative selection in recipients, leading to generation of autoreactive T cells and causing cGVHD. Anti-CD4 mAb treatment promoted immune incompetence of thymus-infiltrating CD8+ T cells, facilitated recovery of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes and regeneration mTECs, and preserved negative-selection, but had no effects on the long-term cellular immunity and humoral immunity, resulting in preservation of GVL effect.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that anti-CD4 mAb therapy early post-HCT allows thymus recovery by inducing the immune tolerance of thymus infiltrated CD8+ T cells, thereby alleviating thymic epithelial cells damage, preserving negative selection, and preserving long-term GVL effect at the same time.
Keywords: CD4 + T cells; anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody; chronic graft-versus-host disease; immune tolerance; thymic recovery.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Li, Fu, Cheng, Zhang, Tang, Yang, Wang and Ni.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial interests that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thymic damage, impaired negative selection, and development of chronic graft-versus-host disease caused by donor CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.J Immunol. 2013 Jul 1;191(1):488-99. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300657. Epub 2013 May 24. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23709681 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of Donor-Origin Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Thymic Epithelial Progenitors Prevents the Development of Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease in Mice.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Jan;6(1):121-130. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0012. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28170174 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease in MHC-Matched Mouse Strains: Genetics, Graft Composition, and Tissue Targets.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019 Dec;25(12):2338-2349. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31415899
-
Immune recovery and the role of recent thymic emigrated T lymphocytes after pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Cytotherapy. 2024 Sep;26(9):980-987. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2024.04.073. Epub 2024 May 1. Cytotherapy. 2024. PMID: 38762804 Review.
-
Hematopoietic cell transplantation for the induction of allo- and xenotolerance.Clin Transplant. 1996 Aug;10(4):357-63. Clin Transplant. 1996. PMID: 8884109 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

