Developmental Changes in Gap Junction Expression in Rat Adrenal Medullary Chromaffin Cells
- PMID: 39776934
- PMCID: PMC11703562
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.24-00033
Developmental Changes in Gap Junction Expression in Rat Adrenal Medullary Chromaffin Cells
Abstract
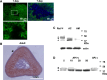
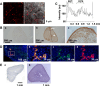
Cell-to-cell communications are desirable for efficient functioning in endocrine cells. Gap junctions and paracrine factors are major mechanisms by which neighboring endocrine cells communicate with each other. The current experiment was undertaken to morphologically examine gap junction expression and developmental changes in rat adrenal medullary chromaffin (AMC) cells. The expression of connexin 43 (Cx43) was conspicuous in the rat adrenal cortex, but not detected immunohistochemically in neonatal or adult AMC cells. Consistent with the morphological findings, the phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms of Cx43 were predominantly and faintly detected by immunoblotting in the adrenal cortical and medullary homogenates, respectively. In contrast to Cx43, Cx36-like immunoreactive (IR) material was detected in neonatal AMC cells, a fraction of which were in the process of migration to the center of the adrenal gland, but this was not seen in adult AMC cells. The current results raise the possibility that the mechanism for cell-to-cell communication changes in a developmental manner in rat AMC cells.
Keywords: chromaffin cell; chromogranin A; connexin; development; gap junction.
2024 The Japan Society of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
VThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Alejandre-Garcia, T., Segura-Chama, P., Perez-Armendariz, E. M., Delgado-Lezama, R. and Hernandez-Cruz, A. (2016) Modulation of spontaneous intracellular Ca2+ fluctuations and spontaneous cholinergic transmission in rat chromaffin cells in situ by endogenous GABA acting on GABAA receptors. Pflugers Arch. 468; 351–365. - PubMed
-
- Arumugam, H., Liu, X., Colombo, P. J, Corriveau, R. A. and Belousov, A. B. (2005) NMDA receptors regulate developmental gap junction uncoupling via CREB signaling. Nature Neurosci. 8; 1720–1726. - PubMed
-
- Barry, D. A., Trimmer, J. S., Merlie, J. P. and Nerbonne, J. M. (1995) Differential expression of voltage-gated K+ channel subunits in adult rat heart. Relation to functional K+ channels? Circ. Res. 77; 361–369. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

