Prognostic effect of CEA, AFP, CA19‑9 and CA242 for recurrence/metastasis of gastric cancer following radical gastrectomy
- PMID: 39776940
- PMCID: PMC11704986
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2024.2812
Prognostic effect of CEA, AFP, CA19‑9 and CA242 for recurrence/metastasis of gastric cancer following radical gastrectomy
Abstract
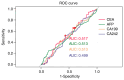
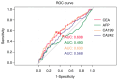
The present study aimed to determine the potential of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), carbohydrate antigen (CA)19-9 and CA242 in predicting recurrence/metastasis of gastric cancer in patients following radical gastrectomy. The clinical data of 368 patients with stage I-III gastric cancer who underwent radical gastrectomy were analyzed, and CEA, AFP, CA19-9 and CA242 levels were detected prior to surgery and 6-12 months following surgery. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to evaluate the potential risk factors for post-operative recurrence/metastasis of gastric cancer, and the predictive value of CEA, AFP, CA19-9 and CA242 levels was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and area under the curve (AUC). Cumulative survival rates were calculated using Kaplan-Meier analysis, and statistical significance was evaluated using a log-rank test. Results of the univariate analysis demonstrated that open surgery, age ≥70, total gastrectomy, disease stage III, and pre-operative CA19-9 and CA242 positivity were risk factors for recurrence/metastasis. ROC curve analysis revealed that the AUC values of postoperative CA19-9 were higher than other values. According to the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, patients with negative CEA, AFP, CA19-9 and CA242 levels prior to surgery exhibited a higher five-year survival rate than those who exhibited positive levels of these tumor markers. In addition, patients with positive CEA, AFP, CA19-9 and CA242 levels prior to surgery exhibited a significantly worse prognosis. Collectively, the results of the present study indicated that CEA, AFP, CA19-9 and CA242 exhibited potential as predictive biomarkers for recurrence/metastasis following radical gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer. Notably, CA19-9 and CA242 may exhibit the highest potential in predicting recurrence/metastasis.
Keywords: gastrectomy; gastric cancer; recurrence/metastasis; tumor marker.
Copyright: © 2024 Luan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
