A comprehensive review of digital twin in healthcare in the scope of simulative health-monitoring
- PMID: 39777066
- PMCID: PMC11705329
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076241304078
A comprehensive review of digital twin in healthcare in the scope of simulative health-monitoring
Abstract
Objective: Digital twins (DTs) emerged in the wake of Industry 4.0 and the creation of cyber-physical systems, motivated by the increased availability and variability of machine and sensor data. DTs are a concept to create a digital representation of a physical entity and imitate its behavior, while feeding real-world data to the digital counterpart, thus allowing enabling digital simulations related to the real-world entity. The availability of new data sources raises the potential for developing structured approaches for prediction and analysis. Similarly, in the field of medicine and digital healthcare, the collection of patient-focused data is rising. Medical DTs, a new concept of structured, exchangeable representations of knowledge, are increasingly used for capturing personal health, targeting specific illnesses, or addressing complex healthcare scenarios in hospitals.
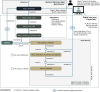
Methods: This article surveys the current state-of-the-art in applying DTs in healthcare, and how these twins are generated to support smart, personalized medicine. These concepts are applied to a DT for a simulated health-monitoring scenario.
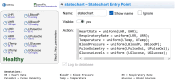
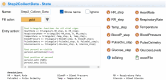
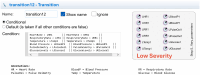
Results: The DT use case is implemented using AnyLogic multi-agent simulation, monitoring the patient's personal health indicators and their development.
Conclusion: The results indicate both possibilities and challenges and provide important insights for future DT implementations in healthcare. They have the potential to optimize healthcare in various ways, such as providing patient-centered health-monitoring.
Keywords: Digital twin; health-monitoring; healthcare; personalized medicine; simulation.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Kaul R, Ossai C, Forkan ARM, et al. The role of AI for developing digital twins in healthcare: the case of cancer care. WIREs Data Min Knowl Discov 2023; 13.
-
- Sittner S, Schuldt J, Gröger S. Digital q-twin: Interoperabilität qualitätsbezogener Daten auf Basis des digitalen Zwilling. In: Woll R and Goldmann C (eds) Trends und Entwicklungstendenzen im Qualitätsmanagement. Wiesbaden: Springer Fachmedien, 2022, pp.83–94.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

