An overview of artificial intelligence based automated diagnosis in paediatric dentistry
- PMID: 39777218
- PMCID: PMC11703950
- DOI: 10.3389/froh.2024.1482334
An overview of artificial intelligence based automated diagnosis in paediatric dentistry
Abstract
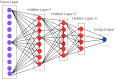
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a subfield of computer science with the goal of creating intelligent machines (1) Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence. In machine learning a datasets are used for training diagnostic algorithms. This review comprehensively explains the applications of AI in the diagnosis in paediatric dentistry. The online database searches were performed between 25th May 2024 to 1st July 2024. Original research studies that focus on the automated diagnosis or predicted the outcome in Paediatric dentistry using AI were included in this review. AI is being used in varied domains of paediatric dentistry like diagnosis of supernumerary and submerged teeth, early diagnosis of dental caries, diagnosis of dental plaques, assessment of bone age, forensic dentistry and preventive oral dental healthcare kit. The field of AI, deep machine learning and CNN's is an upcoming and newer area, with new developments this will open up areas for more sophisticated algorithms in multiple layers to predict accurately, when compared to experienced Paediatric dentists.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; automated diagnosis; convoluted neural network; deep learning; dental caries; dental plaques; paediatric dentistry.
© 2024 Rajinikanth, Rajkumar, Rajinikanth, Anandhapandian and J.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shapiro SC. Artificial Intelligence (AI). Encyclopedia of Computer Science. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley; (2003). p. 89–93.
-
- Chatzimichail E, Feltgen N, Motta L, Empeslidis T, Konstas AG, Gatzioufas Z, et al. Transforming the future of ophthalmology: artificial intelligence and robotics’ breakthrough role in surgical and medical retina advances: a mini review. Front Med. (2024) 11:1434241. 10.3389/fmed.2024.1434241 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nakayama Y, Ohnishi H, Mori M. Association of environmental tobacco smoke with the risk of severe early childhood caries among 3-year-old Japanese children. Caries Res. (2019) 53:268–74. 10.1159/000492790 The performance of the proposed computer-aided diagnosis solution is comparable to the level of experts. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources