Copeptin as biomarker for acute ischemic stroke prognosis and revascularization treatment efficacy
- PMID: 39777314
- PMCID: PMC11705377
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1447355
Copeptin as biomarker for acute ischemic stroke prognosis and revascularization treatment efficacy
Abstract
Introduction: Pro-arginine vasopressin consists of three peptides: arginine-vasopressin, neurophysin II, and copeptin. AVP is released by the neurohypophysis in response to increased plasma osmolality, decreased blood volume and stress. Copeptin has the advantage of being stable ex vivo and easy to measure. New data show the importance of copeptin in ischemic stroke and its complications.
Methods: We present a literature review that highlights the importance of copeptin as a biological marker for stroke. We searched the Pubmed and Scopus databases for papers with the following keywords: "stroke AND copeptin." PRISMA criteria were used.
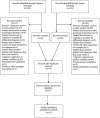
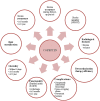
Results: We identified 332 papers that met the criteria. We excluded analyzed reviews, systematic reviews and meta-analyses. 31 articles resulted. The number of patients included in the analyzed studies varied between 18 and 4,302. Copeptin is a marker that associated with clinical stroke severity, infarct volume, short-term and long-term functionality and mortality and adds prognostic value to the previously used scales. It may reflect the effectiveness of revascularization therapy. Copeptin is a biomarker that can help predict post-stroke complications such as: cerebral edema and hemorrhagic transformation.
Discussion: Copeptin is a novel and promising biomarker for evaluating cerebrovascular diseases. Because it is considered a non-specific biomarker, it is not yet used routinely and it cannot replace the clinical examination. However, combined with other clinical or paraclinical parameters, it can increase the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; copeptin; stroke biomarkers; stroke prognosis; treatment efficiency in stroke patients.
Copyright © 2024 Vasile, Tiu and Badiu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Copeptin as a New Blood-Based Marker for Differential Diagnosis in Stroke Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 1;26(11):5328. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115328. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic value of copeptin in patients with acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cardiol J. 2022;29(4):610-618. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2022.0045. Epub 2022 May 27. Cardiol J. 2022. PMID: 35621091 Free PMC article.
-
Copeptin as a biomarker for prediction of prognosis of acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: a meta-analysis.Hypertens Res. 2017 May;40(5):465-471. doi: 10.1038/hr.2016.165. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Hypertens Res. 2017. PMID: 27904159 Review.
-
Copeptin as a surrogate marker for arginine vasopressin: analytical insights, current utility, and emerging applications.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2025 Jan;62(1):24-44. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2024.2383899. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2025. PMID: 39086073 Review.
-
Copeptin Implementation on Stroke Prognosis.Neurol Int. 2023 Jan 16;15(1):83-99. doi: 10.3390/neurolint15010008. Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 36648972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Copeptin as a New Blood-Based Marker for Differential Diagnosis in Stroke Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 1;26(11):5328. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115328. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508137 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blek N, Szwed P, Putowska P, Nowicka A, Drela WL, Gasecka A, et al. . The diagnostic and prognostic value of copeptin in patients with acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiol J. (2022) 29:610–8. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2022.0045, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous