Rnf40 Exacerbates Hypertension-Induced Cerebrovascular Endothelial Barrier Dysfunction by Ubiquitination and Degradation of Parkin
- PMID: 39777866
- PMCID: PMC11707429
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.70210
Rnf40 Exacerbates Hypertension-Induced Cerebrovascular Endothelial Barrier Dysfunction by Ubiquitination and Degradation of Parkin
Abstract
Aims: We aimed to investigate the role of Rnf40 in hypertension-induced cerebrovascular endothelial barrier dysfunction and cognitive impairment.
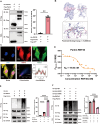
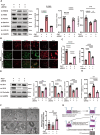
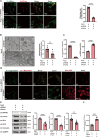
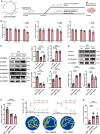
Methods: We employed microarray data analysis and integrated bioinformatics databases to identify a novel E3 ligase, Rnf40, that targets Parkin. To understand the role of RNF40 in hypertension-induced cerebrovascular endothelial cell damage, we used pAAV-hFLT1-MCS-EGFP-3×Flag-mir30shRnf40 to establish an Rnf40-deficient model in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). We also evaluated the cerebrovascular endothelial barrier function, cerebral blood flow, and cognitive performance.
Results: We observed reduced mitophagy in cerebrovascular endothelial cells of SHRs compared with that in Wistar-Kyoto rats. Rnf40 facilitated K48-linked polyubiquitination and degradation of Parkin, thereby inhibiting mitophagy. In the Rnf40-deficient SHR model, knocking down Rnf40 restored mitophagy in cerebrovascular endothelial cells. Additionally, levels of tight junction proteins and cerebrovascular endothelial barrier function improved following Rnf40 downregulation. Rnf40 depletion also improved global cognitive performance and restored cerebral blood flow in SHRs.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that increased Rnf40 levels exacerbate hypertension-induced cerebrovascular endothelial barrier dysfunction by ubiquitinating Parkin.
Keywords: Rnf40; cerebrovascular endothelial barrier; cognition; endothelial cell; hypertension; mitophagy.
© 2025 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mogi M., Ikegawa Y., Haga S., Hoshide S., and Kario K., “Hypertension Facilitates Age‐Related Diseases. ~ Is Hypertension Associated With a Wide Variety of Diseases?,” Hypertension Research 47 (2024): 1246–1259. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022-B042/Gansu Province Education Science and Technology Innovation Project
- YJS-BD-24/Special Fund Project for Doctoral Training of Lanzhou University Second Hospital
- PR0124002/International Science and Technology Cooperation Base
- GSWSKY2017-02/Gansu Province Health Research Project
- CY2021-MS-A13/Cuiying Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Lanzhou University Second Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

