Contemporary Use of Post-Dilatation for Stent Optimization During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention; Results From the Netherlands Heart Registration
- PMID: 39777867
- PMCID: PMC11874260
- DOI: 10.1002/ccd.31404
Contemporary Use of Post-Dilatation for Stent Optimization During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention; Results From the Netherlands Heart Registration
Abstract
Backgrounds: Post-dilatation after stenting with a non-compliant (NC) balloon can be used to improve overall percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) result. Due to lack of evidence on the effect of post-dilatation on adverse clinical endpoints there is no consensus whether post-dilatation should be used routinely. The aim of the current study was to determine the contemporary practice of post-dilatation.
Methods: This study included patients from the Netherlands Heart Registration who underwent PCI between the 4th quarter of 2020 and the 3rd quarter of 2021. The primary endpoint was the rate of post-dilatation with a NC balloon. Secondary endpoints included differences in baseline and procedural characteristics of patients that received post-dilatation and patients that did not receive post-dilatation.
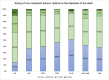
Results: Out of 12,960 patients from 11 hospitals, 49.9% underwent post-dilatation. There was a variety in post-dilatation between hospitals ranging from 29.3% to 82.7% and among operators ranging from 15.9% to 90.5%. Post-dilatation was used less frequent in patients presenting with ST-elevation myocardial infarction or out of hospital cardiac arrest. Multivessel and left main PCI, long stent length and use of intracoronary imaging and calcium modification were associated with increased use of post-dilatation. When imaging was used, the percentage of post-dilatation was 79.4%.
Conclusions: In the Netherlands, stent optimization with post-dilatation using NC balloon is performed in only half of the patients undergoing PCI, with variations in frequency across centres and operators. Post-dilatation is more often used in cases of complex PCI and when intracoronary imaging or calcium modification techniques are used.
Keywords: percutaneous coronary intervention; post‐dilatation; stent optimalization.
© 2025 The Author(s). Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mintz G. S., Popma J. J., Pichard A. D., et al., “Limitations of Angiography in the Assessment of Plaque Distribution in Coronary Artery Disease,” Circulation 93 (1996): 924–931. - PubMed
-
- Stone G. W., Christiansen E. H., Ali Z. A., et al., “Intravascular Imaging‐Guided Coronary Drug‐Eluting Stent Implantation: An Updated Network Meta‐Analysis,” The Lancet 403 (2024): 824–837. - PubMed
-
- Viceconte N., Chan P. H., Barrero E. A., et al., “Frequency Domain Optical Coherence Tomography for Guidance of Coronary Stenting,” International Journal of Cardiology 166 (2013): 722–728. - PubMed
-
- Rana O., Shah N. C., Wilson S., Swallow R., O'kane P., and Levy T., “The Impact of Routine and Intravascular Ultrasound‐Guided High‐Pressure Postdilatation After Drug‐Eluting Stent Deployment: The Stent Optimization (Stop) Study,” The Journal of Invasive Cardiology 26 (2014): 640–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

