Neoadjuvant Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab Versus Chemotherapy in Resectable Lung Cancer
- PMID: 39778121
- PMCID: PMC12005868
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-24-02239
Neoadjuvant Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab Versus Chemotherapy in Resectable Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Neoadjuvant immune checkpoint blockade with nivolumab plus ipilimumab improves overall survival (OS) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however, randomized data for resectable lung cancer are limited. We report results from the exploratory concurrently randomized nivolumab plus ipilimumab and chemotherapy arms of the international phase III CheckMate 816 trial.
Methods: Adults with stage IB-IIIA (American Joint Committee on Cancer seventh edition) resectable NSCLC received three cycles of nivolumab once every 2 weeks plus one cycle of ipilimumab or three cycles of chemotherapy (on day 1 or days 1 and 8 of each 3-week cycle) followed by surgery. Analyses included event-free survival (EFS), OS, pathologic response, surgical outcomes, biomarker analyses, and safety.
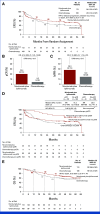
Results: A total of 221 patients were concurrently randomly assigned to nivolumab plus ipilimumab (n = 113) or chemotherapy (n = 108). At a median follow-up of 49.2 months, the median EFS was 54.8 months (95% CI, 24.4 to not reached [NR]) with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus 20.9 months (95% CI, 14.2 to NR) with chemotherapy (HR, 0.77 [95% CI, 0.51 to 1.15]); 3-year EFS rates were 56% versus 44%. Higher rates of EFS events were initially seen, with later benefit favoring nivolumab plus ipilimumab; 3-year OS rates were 73% versus 61% (HR, 0.73 [95% CI, 0.47 to 1.14]); pathologic complete response rates were 20.4% versus 4.6%, respectively. In the respective arms, 83 (74%) and 82 patients (76%) underwent definitive surgery. Grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 14% and 36% of patients, respectively.
Conclusion: Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab showed potential long-term clinical benefit versus chemotherapy, despite early crossing of EFS curves in the preoperative phase and a lower rate of high-grade toxicity.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02998528.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Spicer J, Girard N, Provencio M, et al. : Neoadjuvant nivolumab (NIVO) + chemotherapy (chemo) vs chemo in patients (pts) with resectable NSCLC: 4-year update from CheckMate 816. J Clin Oncol 42, 2024. (suppl 17; abstr LBA8010)
-
- NCCN Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for non-small cell lung cancer. V7.2024. https://www.nccn.org.
-
- Taylor MD, Nagji AS, Bhamidipati CM, et al. : Tumor recurrence after complete resection for non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 93:1813-1820, 2012 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

