Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 39778212
- PMCID: PMC12188811
- DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000002677
Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to compare the efficacy of platelet-rich plasma and corticosteroids in treating plantar fasciitis, focusing on pain relief, foot function, and plantar fascia thickness to identify the optimal treatment approach.
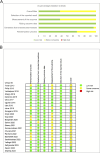
Design: A comprehensive search of medical databases was conducted following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines, utilizing an extensive keyword strategy. Inclusion criteria encompassed prospective randomized controlled trials involving adult patients with plantar fasciitis treated with local platelet-rich plasma or corticosteroid injections, specifically assessing outcomes such as the visual analog scale, American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society scores, and plantar fascia thickness.
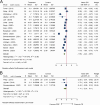
Results: The meta-analysis included 24 randomized controlled trials with 1653 participants. Platelet-rich plasma injections yielded significantly better visual analog scale scores compared to corticosteroid injections at 3 mos ( P = 0.03) and 6 mos ( P < 0.001), with no significant differences at 1 mo ( P = 0.12) and 12 mos ( P = 0.08). American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society scores demonstrated that platelet-rich plasma was superior to corticosteroid at 3 ( P = 0.05), 6 ( P < 0.001), and 12 mos ( P < 0.001), with no significant differences at 1 mo ( P = 0.31). Regarding plantar fascia thickness, there were no significant differences between platelet-rich plasma and corticosteroid at 1-1.5 mos ( P = 0.18), 3 mos ( P = 0.64), and 6 mos ( P = 0.05).
Conclusions: Platelet-rich plasma injections offer superior pain control compared to corticosteroids in the medium term (3-6 mos) but not in the short term or at 1 yr.
Keywords: Corticosteroids; Functional Improvement; Pain Relief; Plantar Fasciitis; Platelet-Rich Plasma.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial disclosure statements have been obtained, and no conflicts of interest have been reported by the authors or by any individuals in control of the content of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Thompson JV Saini SS Reb CW, et al. : Diagnosis and management of plantar fasciitis. J Am Osteopath Assoc 2014;114:900–6 - PubMed
-
- Rabadi D Seo S Wong B, et al. : Immunopathogenesis, early detection, current therapies and prevention of plantar fasciitis: a concise review. Int Immunopharmacol 2022;110:109023. - PubMed
-
- Orchard J: Plantar fasciitis. BMJ 2012;345:e6603. - PubMed
-
- Speed CA: Injection therapies for soft-tissue lesions. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2007;21:333–47 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

