Bariatric surgery for treatment of morbid obesity in adults
- PMID: 39778524
- PMCID: PMC11725483
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2024.219
Bariatric surgery for treatment of morbid obesity in adults
Abstract
Morbid obesity requires active intervention, with treatment options including lifestyle modification, pharmacotherapy, and surgery. As the prevalence of obesity continues to rise in Korea, it is crucial for specialists and general practitioners to have a comprehensive understanding of obesity and its management. Bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment modality for obesity, leading to significant weight loss and metabolic benefits. It involves surgical alterations of normal anatomical structures to improve overall health. Therefore, selecting the appropriate procedure based on the individual characteristics of patients is crucial. This review highlights the two most commonly performed bariatric procedures worldwide, including in Korea: sleeve gastrectomy (SG) and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). Furthermore, it provides a comprehensive overview of the surgical techniques involved in SG and RYGB, addresses potential complications, and presents findings from key studies on the weight loss and metabolic outcomes of these surgeries. Additionally, to support clinical application, the review provides outcome data for these procedures based on studies conducted in Korean populations. In addition to SG and RYGB, this review briefly introduces other surgical and endoscopic options, as well as pharmacological treatments that are currently available or may become viable options in the near future.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Metabolic effect; Morbid obesity; Weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures
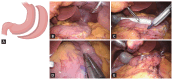
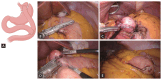
References
-
- Bray GA, Frühbeck G, Ryan DH, Wilding JP. Management of obesity. Lancet. 2016;387:1947–1956. - PubMed
-
- Gossmann M, Butsch WS, Jastreboff AM. Treating the chronic disease of obesity. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105:983–1016. - PubMed
-
- Chang SS, Eisenberg D, Zhao L, et al. Chemerin activation in human obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2016;24:1522–1529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
