RNA sensing at the crossroads of autoimmunity and autoinflammation
- PMID: 39779213
- PMCID: PMC11874990
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.080304.124
RNA sensing at the crossroads of autoimmunity and autoinflammation
Abstract
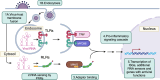
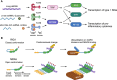
Immune-mediated diseases are common in humans. The immune system is a complex host defense system that evolved to protect us from pathogens, but also plays an important role in homeostatic processes, removing dead or senescent cells, and participating in tumor surveillance. The human immune system has two arms: the older innate immune system and the newer adaptive immune system. Sensing of foreign RNA is critical to the innate immune system's ability to recognize pathogens, especially viral infections. However, RNA sensors are also strongly implicated in autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases, highlighting the importance of balancing pathogen recognition with tolerance to host RNAs that can resemble their viral counterparts. We describe how RNA sensors bind their ligands, how this binding is coupled to upregulation of type I interferon-stimulated genes, and the ways in which mutations in RNA sensors and genes that play important roles in RNA homeostasis have been linked to autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases.
Keywords: RIG-I-like receptors; RNA sensors; Toll-like receptors; autoimmune disease; autoinflammatory disease; type I interferons.
Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Type I Interferonopathies.Annu Rev Med. 2017 Jan 14;68:297-315. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-050715-104506. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Annu Rev Med. 2017. PMID: 27813875 Review.
-
Sterile activation of RNA-sensing pathways in autoimmunity.J Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Dec 20;16(7):mjae029. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjae029. J Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39143032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I interferon-mediated autoinflammation and autoimmunity.Curr Opin Immunol. 2017 Dec;49:96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29128691 Review.
-
Recognition of nucleic acids by pattern-recognition receptors and its relevance in autoimmunity.Immunol Rev. 2011 Sep;243(1):61-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01048.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21884167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleic acid driven sterile inflammation.Clin Immunol. 2013 Jun;147(3):207-15. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Jan 19. Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23419883 Review.
Cited by
-
A tRNA gene potential to activate interferon signaling involves selective termination and is suppressible by La protein/SSB.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 8;53(13):gkaf513. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf513. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40637226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas YM, Laudenbach BT, Martinez-Montero S, Cencic R, Habjan M, Pichlmair A, Damha MJ, Pelletier J, Nagar B. 2017. Structure of human IFIT1 with capped RNA reveals adaptable mRNA binding and mechanisms for sensing N1 and N2 ribose 2′-O methylations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114: E2106–E2115. 10.1073/pnas.1612444114 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
