LncRNA A1BG-AS1 regulates the progress of diabetic foot ulcers via sponging miR-214-3p
- PMID: 39779214
- PMCID: PMC11913556
- DOI: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ24-0440
LncRNA A1BG-AS1 regulates the progress of diabetic foot ulcers via sponging miR-214-3p
Abstract
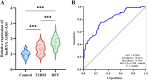
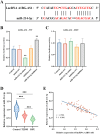
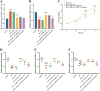
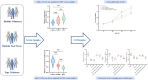
Nerve aberrations and vascular lesions in the distal lower limbs are the etiological factors for diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). This study aimed to understand the regulatory mechanism of angiogenesis in patients with DFU by examining lncRNA, as well as to explore effective targets for diagnosing and treating DFU. The serum levels of A1BG-AS1 and miR-214-3p and the predictive power of A1BG-AS1 for DFU were determined by quantitative PCR and ROC analysis. The correlation of A1BG-AS1 with clinical characteristics was examined using chi-square tests. The risk factors for DFU in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were identified using the logistic regression model. Furthermore, the binding sites of A1BG-AS1 and miR-214-3p were determined. Next, A1BG-AS1 interference plasmid and miR-214-3p inhibitor were co-transfected into high glucose-induced cells to investigate their effects on the expression of angiogenesis-related genes and cell proliferation. The A1BG-AS1 levels were upregulated, whereas the miR-214-3p levels were downregulated in patients with DFU. The upregulation of A1BG-AS1 was significantly associated with both blood glucose levels and ulcer grades. A1BG-AS1 served as a crucial biomarker for diagnosing DFU and evaluating the risk of DFU occurrence in patients with T2DM. Co-transfection experiments revealed that the inhibition of miR-214-3p effectively recovered the suppressive effects of A1BG-AS1 on angiogenesis-related gene expression, endothelial cell differentiation, and proliferation. The sponging effect of A1BG-AS1 on miR-214-3p impaired angiogenesis in patients with DFU. Thus, A1BG-AS1 is a potential therapeutic target for DFU.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Diabetic foot ulcers; Diagnostic; LncRNA; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-23c regulates wound healing by targeting stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α/CXCL12) among patients with diabetic foot ulcer.Microvasc Res. 2020 Jan;127:103924. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2019.103924. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Microvasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31520606
-
A1BG-AS1 promotes the biological functions of osteosarcoma cells via regulating the microRNA-148a-3p/USP22 axis and stabilizing the expression of SIRT1 through deubiquitinase function.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2023 Jul-Dec;27(10):1017-1029. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2023.2263908. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2023. PMID: 37747800
-
Decreased expression of miR-204-3p in peripheral blood and wound margin tissue associated with the onset and poor wound healing of diabetic foot ulcers.Int Wound J. 2023 Feb;20(2):413-429. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13890. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Int Wound J. 2023. PMID: 35879811 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA DLEU1 promotes angiogenesis in diabetic foot ulcer wound healing by regulating miR-96-5p.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Feb;193(1):241-247. doi: 10.1007/s11845-023-03471-x. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 37515685
-
Long noncoding RNA H19 acts as a miR-29b sponge to promote wound healing in diabetic foot ulcer.FASEB J. 2021 Jan;35(1):e20526. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900076RRRRR. Epub 2020 Nov 10. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33174326
References
-
- Rehman ZU, Khan J, Noordin S (2023) Diabetic foot ulcers: contemporary assessment and management. J Pak Med Assoc 73: 1480–1487. - PubMed
-
- Ping J, Li L, Dong Y, Wu X, Huang X, et al. (2022) The role of long non-coding RNAs and circular RNAs in bone regeneration: modulating miRNAs function. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 16: 227–243. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

