Microglia depletion reduces neurodegeneration and remodels extracellular matrix in a mouse Parkinson's disease model triggered by α-synuclein overexpression
- PMID: 39779738
- PMCID: PMC11711755
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-024-00846-4
Microglia depletion reduces neurodegeneration and remodels extracellular matrix in a mouse Parkinson's disease model triggered by α-synuclein overexpression
Abstract
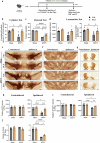
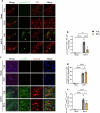
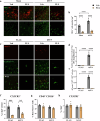
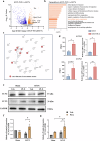
Chronic neuroinflammation with sustained microglial activation occurs in Parkinson's disease (PD), yet the mechanisms and exact contribution of these cells to the neurodegeneration remains poorly understood. In this study, we induced progressive dopaminergic neuron loss in mice via rAAV-hSYN injection to cause the neuronal expression of α-synuclein, which produced neuroinflammation and behavioral alterations. We administered PLX5622, a colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor inhibitor, for 3 weeks prior to rAAV-hSYN injection, maintaining it for 8 weeks to eliminate microglia. This chronic treatment paradigm prevented the development of motor deficits and concomitantly preserved dopaminergic neuron cell and weakened α-synuclein phosphorylation. Gene expression profiles related to extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling were increased after microglia depletion in PD mice, which were further validated on protein level. We demonstrated that microglia exert adverse effects during α-synuclein-overexpression-induced neuronal lesion formation, and their depletion remodels ECM and aids recovery following insult.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
- 7222005/Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality (Beijing Natural Science Foundation)
- KM202010025032/Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (Beijing Municipal Education Commission)
- 32171158/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31971094/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

