SIX1 aggravates the progression of spinal cord injury in mice by promoting M1 polarization of microglia
- PMID: 39779741
- PMCID: PMC11711668
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82121-3
SIX1 aggravates the progression of spinal cord injury in mice by promoting M1 polarization of microglia
Abstract
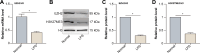
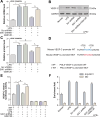
Inflammation aggravates secondary damage following spinal cord injury (SCI). M1 microglia induce inflammation and exert neurotoxic effects, whereas M2 microglia exert anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. The sine oculis homeobox (SIX) gene family consists of six members, including sine oculis homeobox homolog 1 (SIX1)-SIX6. SIX1 is expressed in microglia and promotes inflammation. This study aimed to evaluate the role and underlying mechanisms of SIX1 in microglia polarization in vitro (LPS-treated mouse microglia; BV2 cells) and in vivo (a mouse model of SCI). SIX1 expression was increased in the microglia of mice with SCI. SIX1 was positively correlated with the M1 microglia marker inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and negatively correlated with the M2 microglia marker arginase 1 (Arg1) in mice with SCI. Knockdown of SIX1 promoted functional recovery by enhancing M2 microglia polarization in mice with SCI. The transcription, expression, and activity of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) were decreased in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells. Downregulation of EZH2 promoted SIX1 expression in LPS-treated BV2 cells by inhibiting the methylation of the SIX1 promoter. SIX1 enhanced the transcription of vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells with downregulated EZH2. VEGF-C promoted M1 polarization and inhibited M2 polarization in BV2 cells by binding to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR3). Overall, the results suggest that SIX1 promotes M1 polarization of microglia following SCI by upregulating the VEGF-C/VEGFR3 axis, whereas the blockade of SIX1 can improve the recovery of locomotor function following SCI, demonstrating a novel strategy for the treatment of SCI.
Keywords: Microglia; Polarization; Sine oculis homeobox homolog 1 (SIX1); Spinal cord injury (SCI); Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: We confirm that all experimental protocols conducted in this study were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University. We confirm that all methods used in this study were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. The study was carried out in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

