Conformational protection of molybdenum nitrogenase by Shethna protein II
- PMID: 39779845
- PMCID: PMC11754109
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-08355-3
Conformational protection of molybdenum nitrogenase by Shethna protein II
Abstract
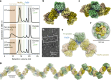
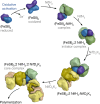
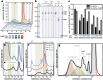
The oxygen-sensitive molybdenum-dependent nitrogenase of Azotobacter vinelandii is protected from oxidative damage by a reversible 'switch-off' mechanism1. It forms a complex with a small ferredoxin, FeSII (ref. 2) or the 'Shethna protein II'3, which acts as an O2 sensor and associates with the two component proteins of nitrogenase when its [2Fe:2S] cluster becomes oxidized4,5. Here we report the three-dimensional structure of the protective ternary complex of the catalytic subunit of Mo-nitrogenase, its cognate reductase and the FeSII protein, determined by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. The dimeric FeSII protein associates with two copies of each component to assemble a 620 kDa core complex that then polymerizes into large, filamentous structures. This complex is catalytically inactive, but the enzyme components are quickly released and reactivated upon oxygen depletion. The first step in complex formation is the association of FeSII with the more O2-sensitive Fe protein component of nitrogenase during sudden oxidative stress. The action of this small ferredoxin represents a straightforward means of protection from O2 that may be crucial for the maintenance of recombinant nitrogenase in food crops.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





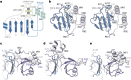

References
-
- Robson, R. L. & Postgate, J. R. Oxygen and hydrogen in biological nitrogen fixation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol.34, 183–207 (1980). - PubMed
-
- Shethna, Y. I., DerVartanian, D. V. & Beinert, H. Non heme (iron-sulfur) proteins of Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.31, 862–868 (1968). - PubMed
-
- Moshiri, F., Kim, J. W., Fu, C. L. & Maier, R. J. The FeSII protein of Azotobacter vinelandii Is not essential for aerobic nitrogen fixation, but confers significant protection to oxygen-mediated inactivation of nitrogenase in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Microbiol.14, 101–114 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Schlesier, J., Rohde, M., Gerhardt, S. & Einsle, O. A conformational switch triggers nitrogenase protection from oxygen damage by Shethna protein II (FeSII). J. Am. Chem. Soc.138, 239–247 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

