Bidirectional histone monoaminylation dynamics regulate neural rhythmicity
- PMID: 39779849
- PMCID: PMC11754111
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-08371-3
Bidirectional histone monoaminylation dynamics regulate neural rhythmicity
Abstract
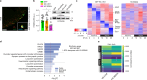
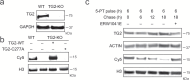
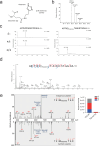
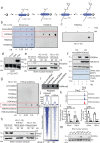
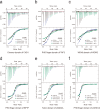
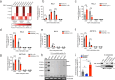
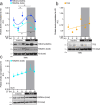
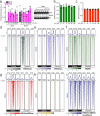
Histone H3 monoaminylations at Gln5 represent an important family of epigenetic marks in brain that have critical roles in permissive gene expression1-3. We previously demonstrated that serotonylation4-10 and dopaminylation9,11-13 of Gln5 of histone H3 (H3Q5ser and H3Q5dop, respectively) are catalysed by transglutaminase 2 (TG2), and alter both local and global chromatin states. Here we found that TG2 additionally functions as an eraser and exchanger of H3 monoaminylations, including H3Q5 histaminylation (H3Q5his), which displays diurnally rhythmic expression in brain and contributes to circadian gene expression and behaviour. We found that H3Q5his, in contrast to H3Q5ser, inhibits the binding of WDR5, a core member of histone H3 Lys4 (H3K4) methyltransferase complexes, thereby antagonizing methyltransferase activities on H3K4. Taken together, these data elucidate a mechanism through which a single chromatin regulatory enzyme has the ability to sense chemical microenvironments to affect the epigenetic states of cells, the dynamics of which have critical roles in the regulation of neural rhythmicity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 DA047233/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM115327/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116900/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007135/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM086868/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM138386/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030286/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA056595/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM086868/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM150676/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA192937/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

