Copper and nickel doped carbon dots for rapid and sensitive fluorescent turn-off detection of bilirubin
- PMID: 39779895
- PMCID: PMC11711382
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-85246-1
Copper and nickel doped carbon dots for rapid and sensitive fluorescent turn-off detection of bilirubin
Abstract
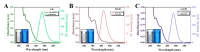
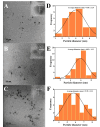
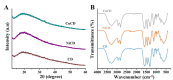
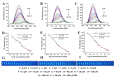
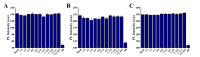
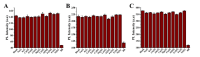
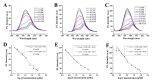
Carbon dots doped with metals and non-metals have gained much popularity due to the enhancement in their optical and electronic properties. In this study, polyethyleneimine-functionalized transition metal (nickel or copper) doped carbon dots (CD, NiCD and CuCD) were synthesized through hydrothermal method. The carbon dots exhibited a blue fluorescence at 470 nm when excited at 350 nm. The as-synthesized carbon dots were utilised for the fluorimetric detection of bilirubin in the range 0.5 µM - 280 µM, with CuCD exhibiting the highest sensitivity of 155.38 a.u/log µM in the concentration range 0.5 to 10 µM and 84.01 a.u/ log µM in the concentration range 10 to 280 µM. CuCD also exhibited the lowest limit of detection of 0.0907 µM and the lowest limit of quantification of 0.3023 µM. All the carbon dots showed negligible interference in the presence of biomolecules and metal ions present in human serum implying the remarkable selectivity of the method to bilirubin detection. Further, the carbon dots were successfully tested for their real-time application in human serum using bilirubin-spiked serum samples.
Keywords: Bilirubin; Biosensor; Carbon dots; Copper-doped carbon dots; Fluorescence quenching; Nickel-doped carbon dots.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluorescent Nitrogen-doped Carbon Dots-based Turn-off Sensor for Bilirubin.J Fluoresc. 2025 May;35(5):3565-3576. doi: 10.1007/s10895-024-03771-0. Epub 2024 Jun 12. J Fluoresc. 2025. PMID: 38865062
-
Metal and heteroatoms co-doped fluorescent carbon dots for highly selective and sensitive detection of Mg2+ ions in aqueous media: Applications in test strips, pharmaceutical, real samples and bioimaging.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2025 May 5;332:125851. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2025.125851. Epub 2025 Feb 8. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2025. PMID: 39923716
-
Turn-Off Fluorometric Determination of Bilirubin Using Facile Synthesized Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent Probe.J Fluoresc. 2025 Feb;35(2):963-974. doi: 10.1007/s10895-023-03572-x. Epub 2024 Jan 13. J Fluoresc. 2025. PMID: 38217780
-
Carbon quantum dots in spectrofluorimetric analysis: A comprehensive review of synthesis, mechanisms and multifunctional applications.Talanta. 2025 Oct 1;293:128066. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2025.128066. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Talanta. 2025. PMID: 40194462 Review.
-
Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications in the Detection of Bilirubin - Recent Advances and Challenges.J Fluoresc. 2025 May 27. doi: 10.1007/s10895-025-04366-z. Online ahead of print. J Fluoresc. 2025. PMID: 40423933 Review.
Cited by
-
Mn-Doped Carbon Dots as Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance and Fluorescence Imaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 29;26(13):6293. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136293. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ji, C., Zhou, Y., Leblanc, R. M. & Peng, Z. Recent developments of Carbon dots in Biosensing: a review. ACS Sens.5, 2724–2741 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Wang, F. T., Wang, L. N., Xu, J., Huang, K. J. & Wu, X. Synthesis and modification of carbon dots for advanced biosensing application. Analyst146, 4418–4435 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Tejwan, N. et al. Metal-doped and hybrid carbon dots: a comprehensive review on their synthesis and biomedical applications. J. Controlled Release. 330, 132–150 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Li, X. et al. Metal ions-doped carbon dots: synthesis, properties, and applications. Chem. Eng. J.430, 133101 (2022).
-
- Wang, X., Chowdhury, J. R. & Chowdhury, N. R. Bilirubin metabolism: Applied physiology. Curr. Paediatrics. 16, 70–74 (2006).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

