Remotely delivered weight management for people with long COVID and overweight: the randomized wait-list-controlled ReDIRECT trial
- PMID: 39779922
- PMCID: PMC11750722
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03384-x
Remotely delivered weight management for people with long COVID and overweight: the randomized wait-list-controlled ReDIRECT trial
Abstract
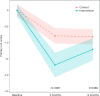
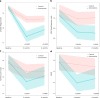
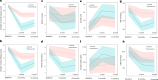
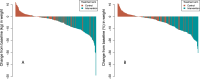
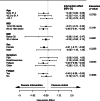
Long COVID (LC) is a complex multisymptom condition with no known disease-modifying treatments. This wait-list-controlled open-label trial tested whether a remotely delivered structured weight management program could improve respective LC symptoms in people living with overweight. Adults with LC (symptoms >12 weeks) and body mass index >27 kg m-2 (>25 kg m-2 for South Asians) were randomized (n = 234, 1:1) to control (n = 116, usual care) or the remotely delivered structured weight management (n = 118, total diet replacement (850 kcal per day) for 12 weeks, followed by food reintroduction and weight loss maintenance support) via minimization and randomization (80:20) to balance dominant LC symptom, sex, age, ethnicity and postcode-based index of multiple deprivation between groups. The control group received the intervention after 6 months. Participants selected the dominant LC symptom they would most like to improve (fatigue, breathlessness, pain, anxiety/depression or other) as the prespecified respective primary outcome. Individual symptoms were assessed using validated questionnaires and a visual analog scale for those without prespecified scales. At 6 months, the primary outcome improved in the intervention group (change -1.16 (s.d. 1.42), n = 97 analyzed) compared with the control group (change -0.83 (s.d. 1.14), n = 117 analyzed) with a treatment effect of -0.34 (95% confidence interval -0.67 to -0.01), with no excess of serious adverse events. International Standard Randomised Controlled Trial Number Registry registration: ISRCTN 12595520 .
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: N.B. is an employee and shareholder of Counterweight Ltd, subcontracted to the University of Glasgow to deliver the ReDIRECT intervention. A.M. is a member of Clinical Steering Committee for ARC Medical Inc. N.S. has received institutional grant support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis and Roche Diagnostics and honoraria from Abbott Laboratories, AbbVie, Afimmune, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Hanmi Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Menarini-Ricerche, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche Diagnostics and Sanofi. M.E.J.L. has received lecturing fees from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Nestle and Sanofi and is a medical advisor to Counterweight Ltd, with fees paid to the University of Glasgow. J.O. and C.W. are members of the Long Covid Scotland charity. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

