Transcript-specific enrichment enables profiling of rare cell states via single-cell RNA sequencing
- PMID: 39779958
- PMCID: PMC12276987
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-02036-7
Transcript-specific enrichment enables profiling of rare cell states via single-cell RNA sequencing
Abstract
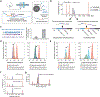
Single-cell genomics technologies have accelerated our understanding of cell-state heterogeneity in diverse contexts. Although single-cell RNA sequencing identifies rare populations that express specific marker transcript combinations, traditional flow sorting requires cell surface markers with high-fidelity antibodies, limiting our ability to interrogate these populations. In addition, many single-cell studies require the isolation of nuclei from tissue, eliminating the ability to enrich learned rare cell states based on extranuclear protein markers. In the present report, we addressed these limitations by developing Programmable Enrichment via RNA FlowFISH by sequencing (PERFF-seq), a scalable assay that enables scRNA-seq profiling of subpopulations defined by the abundance of specific RNA transcripts. Across immune populations (n = 184,126 cells) and fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded brain tissue (n = 33,145 nuclei), we demonstrated that programmable sorting logic via RNA-based cytometry can isolate rare cell populations and uncover phenotypic heterogeneity via downstream, high-throughput, single-cell genomics analyses.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A.T.S. is a founder of Immunai, Cartography Biosciences, Santa Ana Bio and Prox Biosciences, an advisor to Wing Venture Capital and receives research funding from Astellas and Merck Research Laboratories. R.R.S., L.S.L. and C.A.L. are consultants to Cartography Biosciences. R.C. is a consultant for Sanavia Oncology, S2 Genomics and LevitasBio. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



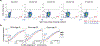

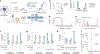

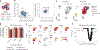
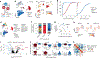
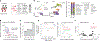

Update of
-
Transcript-specific enrichment enables profiling rare cell states via scRNA-seq.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 27:2024.03.27.587039. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.27.587039. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Genet. 2025 Feb;57(2):451-460. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-02036-7. PMID: 38586040 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UM1 HG012076/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1HG012076/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- R00 HG012579/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AT012984/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA008748/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

