High incidence of radiation-induced brain necrosis in the periventricular deep white matter: stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases using volumetric modulated arc therapy
- PMID: 39780156
- PMCID: PMC11715558
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-024-02579-3
High incidence of radiation-induced brain necrosis in the periventricular deep white matter: stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases using volumetric modulated arc therapy
Abstract
Purpose: In this retrospective study, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy and incidence of radiation-induced brain necrosis (RBN) after volumetric modulated arc therapy-based stereotactic irradiation (VMAT-STI) for brain metastases.
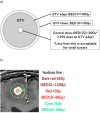
Methods: In the 220 brain metastatic lesions included between January 2020 and June 2022, there were 1-9 concurrently treated lesions (median 1). A biologically effective dose (BED)10 of 80 Gy and a reduced BED10 of 50 Gy were prescribed to the gross tumor volume (GTV) and planning target volume (PTV) (PTV = GTV + 3 mm) margins, respectively. The number of fractions was adjusted from 3 to 15 to accommodate different GTV sizes; for larger tumor volumes, this was increased while maintaining the BED10 values comparable to those for GTV and PTV margins.
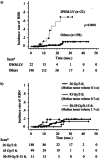
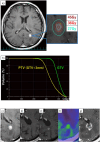
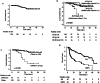
Results: Of the total patients, 16 (7%) exhibited locally progressive lesions; local tumor recurrence was observed in 2 (1%) patients, while RBN was noted in 14 (6%) patients. RBN was significantly more prevalent in the deep white matter around the lateral ventricles (DWM-LV) than in other sites, occurring in 9/22 (41%) lesions of metastases in the DWM-LV. The 2-year actuarial incidence risk of developing RBN was significantly higher in the DWM-LV (69%) than at other sites (5%).
Conclusion: The recurrence rate of brain metastases was low, and the incidence of RBN was lower in tumor sites other than the DWM-LV. However, the frequency of RBN was significantly higher in the DWM-LV region. Additional VMAT-STI-prescribed dose protocols are necessary to reduce RBN incidence in DWM-LVs.
Keywords: Radiation-induced brain necrosis; Stereotactic radiotherapy; Volumetric modulated arc therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Our study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of University of Occupational and Environmental health. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Human Ethics declaration: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bijl HP, van Luijk P, Coppes RP, et al. Regional differences in radiosensitivity across the rat cervical spinal cord. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61(2):543–51. - PubMed
-
- Steen RG, Spence D, Wu S, et al. Effect of therapeutic ionizing radiation on the human brain. Ann Neurol. 2001;50(6):787–95. - PubMed
-
- Ohtakara K, Hayashi S, Nakayama N, et al. Significance of target location relative to the depth from the brain surface and high-dose irradiated volume in the development of brain radionecrosis after micromultileaf collimator-based stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Neurooncol. 2012;108(1):201–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

