MORF4L2 induces immunosuppressive microenvironment and immunotherapy resistance through GRHL2/MORF4L2/H4K12Ac/CSF1 axis in triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 39780291
- PMCID: PMC11715975
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-024-00719-1
MORF4L2 induces immunosuppressive microenvironment and immunotherapy resistance through GRHL2/MORF4L2/H4K12Ac/CSF1 axis in triple-negative breast cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: MORF4L2 induces immunosuppressive microenvironment and immunotherapy resistance through GRHL2/MORF4L2/H4K12Ac/CSF1 axis in triple-negative breast cancer.Biomark Res. 2025 Feb 13;13(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00743-9. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 39948640 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Although immunotherapy has achieved great progress in advanced triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), there are still numerous patients who do not benefit from immunotherapy. Therefore, identification of the key molecule that induces immune escape and clarification of its specific mechanism in TNBC are urgently needed.
Methods: In this research, single cell sequencing and bulk sequencing were conducted for biomarker screening. Immunohistochemistry, multiplex immunofluorescence, and orthotopic TNBC tumor model were applied in identifying the key molecule driving immune escape. At the mechanical level, RNA sequencing, in vitro co-culturing system, flow cytometry, Western blotting, ELISA, and real-time qPCR were carried out.
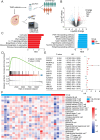
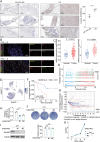
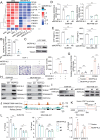
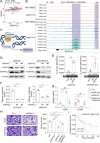
Results: Mortality factor 4 like 2 (MORF4L2) expression is significantly up-regulated among patients who developed anti-PD1 resistance. MORF4L2 enhances anti-PD1 resistance by inducing the chemotaxis of macrophage infiltration and promoting their polarization towards the alternative activation phenotype (M2), thus creating an immunosuppressive microenvironment. Mechanistically, MORF4L2 actes as part of NuA4 histone acetyltransferase (HAT) complex, contributes to to histone 4 lysine 12 acetylation (H4K12Ac) and activates the downstream transcription of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF1). CSF1 is secreted by tumor cells and binds to the macrophage-surface CSF1 receptor (CSF1R), which chemotactically converted and polarized macrophages to the M2 phenotype. Furthermore, we revealed that grainyhead like transcription factor 2 (GRHL2) could promote MORF4L2 transcription by binding to the MORF4L2 enhancer region. Notably, BLZ549, an inhibitor of CSF1R, restored the anti-PD1 sensitivity by blocking the GRHL2/MORF4L2/H4K12Ac/CSF1 axis.
Conclusions: GRHL2/MORF4L2/H4K12Ac/CSF1 axis plays an important role in anti-PD1 resistance. CSF1R inhibitors can reverse GRHL2/MORF4L2-mediated anti-PD1 resistance.
Keywords: Anti-PD1; Combination therapy; Histone 4 lysine 12 acetylation; Mortality factor 4 like 2; Triple-negative breast cancer; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. All authors critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM, Goss PE. Breast cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(7):e279-289. - PubMed
-
- Harbeck N, Penault-Llorca F, Cortes J, Gnant M, Houssami N, Poortmans P, Ruddy K, Tsang J, Cardoso F. Breast cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):66. - PubMed
-
- Leon-Ferre RA, Goetz MP. Advances in systemic therapies for triple negative breast cancer. BMJ. 2023;381:e071674. - PubMed
-
- Bianchini G, De Angelis C, Licata L, Gianni L. Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast cancer - expanded options, evolving needs. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19(2):91–113. - PubMed
-
- Jia H, Truica CI, Wang B, Wang Y, Ren X, Harvey HA, Song J, Yang JM. Immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer: existing challenges and exciting prospects. Drug Resist Updat. 2017;32:1–15. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

