Fetal growth restriction adversely impacts trajectory of hippocampal neurodevelopment and function
- PMID: 39780443
- PMCID: PMC12145903
- DOI: 10.1111/bpa.13330
Fetal growth restriction adversely impacts trajectory of hippocampal neurodevelopment and function
Abstract
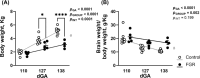
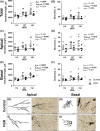
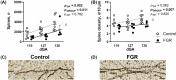
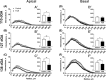
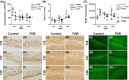
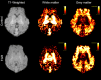
The last pregnancy trimester is critical for fetal brain development but is a vulnerable period if the pregnancy is compromised by fetal growth restriction (FGR). The impact of FGR on the maturational development of neuronal morphology is not known, however, studies in fetal sheep allow longitudinal analysis in a long gestation species. Here we compared hippocampal neuron dendritogenesis in FGR and control fetal sheep at three timepoints equivalent to the third trimester of pregnancy, complemented by magnetic resonance image for brain volume, and electrophysiology for synaptic function. We hypothesized that the trajectory of hippocampal neuronal dendrite outgrowth would be decreased in the growth-restricted fetus, with implications for hippocampal volume, connectivity, and function. In control animals, total dendrite length increased with advancing gestation, but not in FGR, resulting in a significantly reduced trajectory of dendrite outgrowth in FGR fetuses for total length, branching, and complexity. Ex vivo electrophysiology analysis shows that paired-pulse facilitation was reduced in FGR compared to controls for cornu ammonis 1 hippocampal outputs, reflecting synaptic dysfunction. Hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor density decreased over late gestation in FGR fetuses but not in controls. This study reveals that FGR is associated with a significant deviation in the trajectory of dendrite outgrowth of hippocampal neurons. Where dendrite length significantly increased over the third trimester of pregnancy in control brains, there was no corresponding increase over time in FGR brains, and the trajectory of dendrite outgrowth in FGR offspring was significantly reduced compared to controls. Reduced hippocampal dendritogenesis in FGR offspring has severe implications for the development of hippocampal connectivity and long-term function.
Keywords: FGR; IUGR; MRI; brain injury; brain volume; electrophysiology; preterm.
© 2025 The Author(s). Brain Pathology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society of Neuropathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
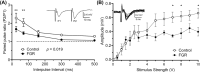
References
-
- Dall'Asta A, Melito C, Morganelli G, Lees C, Ghi T. Determinants of placental insufficiency in fetal growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2023;61(2):152–157. - PubMed
-
- Gordijn SJ, Beune IM, Thilaganathan B, Papageorghiou A, Baschat AA, Baker PN, et al. Consensus definition of fetal growth restriction: a Delphi procedure. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016;48(3):333–339. - PubMed
-
- Lees CC, Stampalija T, Baschat AA, da Silva Costa F, Ferrazzi E, Figueras F, et al. ISUOG practice guidelines: diagnosis and management of small‐for‐gestational‐age fetus and fetal growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2020;56(2):298–312. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

