Eyelid Spindle Cell Lipoma: Case Report and Review of Three Patients in Literature
- PMID: 39780903
- PMCID: PMC11706713
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.70097
Eyelid Spindle Cell Lipoma: Case Report and Review of Three Patients in Literature
Abstract
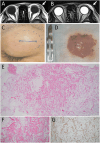
A 39-year-old woman presented a saucer-shaped mass in the left upper eyelid and underwent the extirpation at local anesthesia. Pathologically, collagen fibers, capillaries, small vessels, and CD34-positive spindle cells were dispersed among mature adipose tissues, indicative of spindle cell lipoma. Long-lasting cyst-like eyelid masses would be usually dermoid cysts, and spindle cell lipoma would be listed as a rare pathological diagnosis in differential diagnoses of cyst-like lesions in the upper and lower eyelid.
Keywords: CD34; eyelid; orbital bony edge; pathology; spindle cell lipoma.
© 2025 The Author(s). Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spindle cell lipoma of the knee: a case report.J Orthop Sci. 2004;9(1):86-9. doi: 10.1007/s00776-003-0745-4. J Orthop Sci. 2004. PMID: 14767709
-
Hypopharyngeal spindle cell lipoma: A case report and review of literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 May 7;100(18):e25782. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025782. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33950973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suprasellar spindle cell lipoma.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2009 Jun;13(3):173-5. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2008.12.006. Epub 2009 Feb 5. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19433296
-
Intramuscular lipoma of the eyelid.Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 2000 Jul-Aug;31(4):340-1. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 2000. PMID: 10928675
-
Spindle Cell Lipoma Arising from the Supraglottis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Head Neck Pathol. 2021 Dec;15(4):1299-1302. doi: 10.1007/s12105-020-01259-4. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Head Neck Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33394369 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meyer A., “The Broadening Spectrum of Spindle Cell Lipoma and Related Tumors: A Review,” Human Pathology Reports 28 (2022): 300646.
-
- Johnson B. L. and J. G. Linn, Jr. , “Spindle Cell Lipoma of the Orbit,” Archives of Ophthalmology 97 (1979): 133–134. - PubMed
-
- Bartley G. B., Yeatts R. P., Garrity J. A., Farrow G. M., and Campbell R. J., “Spindle Cell Lipoma of the Orbit,” American Journal of Ophthalmology 100 (1985): 605–609. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

