A newly proposed endoscopic score system to evaluate the entire small bowel and predict the prognosis in Crohn's disease
- PMID: 39780925
- PMCID: PMC11704775
- DOI: 10.18999/nagjms.86.4.608
A newly proposed endoscopic score system to evaluate the entire small bowel and predict the prognosis in Crohn's disease
Abstract
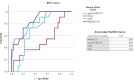
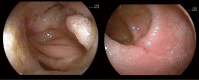
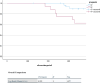
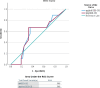
Small bowel stenosis in patients with Crohn's disease leads to abdominal symptoms and can affect prognosis. The Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease for the large bowel has been applied to the small bowel; however, stenosis scoring may be overestimated since it has a long diameter. This retrospective study aimed to devise a new endoscopic scoring system including the small bowel and evaluate whether it predicts the prognosis of Crohn's disease. The study included 103 patients with Crohn's disease at our hospital. We modified the Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease and proposed a new scoring system; the modified applied Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease was created by subtracting one point for stricture from the Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to assess the accuracy of the modified applied score for Crohn's disease in predicting disease worsening within 1 year. Results were validated using the log-rank test. For the modified applied score, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for disease worsening within 1 year in 57 cases was 0.850. When the cutoff score was set to 9 points, the sensitivity and specificity were 72.7% and 80.6%, respectively. The log-rank test showed a significant difference (P = 0.027) in the risk of worsening within 1 year between the low (<9 points) and high (≥9 points) score groups. Thus, a higher modified applied Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease may be associated with a significantly increased risk of disease worsening within 1 year.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; balloon-assisted endoscopy; prognosis; scoring; small bowel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of endoscopic activity scores in patients with Crohn's disease based on a post hoc analysis of data from SONIC.Gastroenterology. 2013 Nov;145(5):978-986.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.010. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23954314 Clinical Trial.
-
Determining the Accuracy and Interobserver Agreement of 4 Ultrasound Scores in Crohn's Disease Assessment: Correlations With Endoscopy.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 1;16(4):e00812. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000812. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39791555 Free PMC article.
-
Level of Fecal Calprotectin Correlates With Severity of Small Bowel Crohn's Disease, Measured by Balloon-assisted Enteroscopy and Computed Tomography Enterography.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jan;15(1):56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.08.015. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27565523
-
Endoscopic scoring systems for the evaluation and monitoring of disease activity in Crohn's disease.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb-Apr;38-39:101616. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 May 28. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31327405 Review.
-
Inter- and Intraobserver Variability on Endoscopic Scoring Systems in Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024 Nov 4;30(11):2217-2226. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izae051. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024. PMID: 38547325
References
-
- Turner D, Ricciuto A, Lewis A, et al. STRIDE-II: an Update on the Selecting Therapeutic Targets in inflammatory bowel Disease (STRIDE) Initiative of the International Organization for the Study of IBD (IOIBD): determining therapeutic goals for treat-to-target strategies in IBD. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(5):1570–1583. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.12.031. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
