Study on wettability of water stemming for blasting dust adjusted by surfactants and inorganic salts
- PMID: 39780971
- PMCID: PMC11706644
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.241250
Study on wettability of water stemming for blasting dust adjusted by surfactants and inorganic salts
Abstract
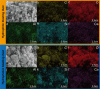
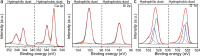
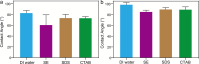
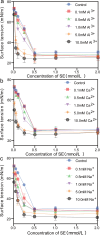
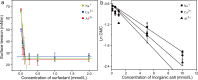
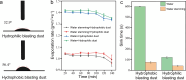
Water stemming is an efficient method of removing blasting dust by wetting. There is still a lack of methods for rapid optimization of water stemming components with high wettability. Herein, blasting dust was collected from a tunnel in Chongqing (China) to investigate its removal performance by different water stemmings. The two most important components of blasting dust were SiO2 and CaCO3 by characterization analysis. Notably, hydrophilic blasting dust has significantly more SiO2 than hydrophobic blasting dust. The density functional theory calculation predicted the wettability of water stemming containing sucrose fatty acid ester (SE) higher than that of water stemming containing other surfactants. Moreover, the water contact angle and surface tension experiments determined the addition of inorganic salts to the water stemming containing SE could increase its wettability, with the addition of Al3+ giving the best performance. The sink test and water retention experiment further prove that our synthesized water stemming has a good wetting ability on both hydrophobic and hydrophilic blasting dust. The findings of this study advance the development of reliable methods for optimizing water stemming with high wettability for removing the blasting dust.
Keywords: blasting dust; inorganic salts; surfactants; water stemming; wettability.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kumar P, Mohammadi H, Chopra R, Kumar Tyagi S, Kumar Pandey S. 2023. A newly developed blasting cut in tunnels; application of ‘combined method’ in small to medium-sized tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 142, 105426. ( 10.1016/j.tust.2023.105426) - DOI
-
- Sun Z, Zhang D, Fang Q. 2023. Technologies for large cross-section subsea tunnel construction using drilling and blasting method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 141, 105161. ( 10.1016/j.tust.2023.105161) - DOI
-
- Shi J, Zhang W, Guo S, An H. 2022. Numerical modelling of blasting dust concentration and particle size distribution during tunnel construction by drilling and blasting. Metals 12, 547. ( 10.3390/met12040547) - DOI
-
- Fu J, Hu L, Hu M. 2022. Investigating blasting demolition dust micromorphology, microscopic agglomeration process with wetting droplet and suppression effectiveness by explosion water mist. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 883386. ( 10.3389/fenvs.2022.883386) - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
