Prototheca osteomyelitis in a dog
- PMID: 39781412
- PMCID: PMC11705177
Prototheca osteomyelitis in a dog
Abstract
Canine systemic protothecosis is an uncommon disease caused by Prototheca spp., which are saprophytic algae occurring ubiquitously in nature. Infection occurs most commonly in immunocompromised animals. Most infected dogs have chronic large-bowel diarrhea, ocular lesions, neurologic deficits, or a combination thereof, but various tissues can be affected. This case highlights a unique presentation of protothecosis in a dog, in which lameness resulting from osteomyelitis was the predominant clinical sign. Key clinical message: Although osteomyelitis is an atypical manifestation, protothecosis can be a differential diagnosis for an aggressive bony lesion and is particularly worthy of consideration in immunocompromised dogs.
Ostéomyélite à Prototheca chez un chienLa protothécose systémique canine est une maladie rare causée par Prototheca spp., une algue saprophyte omniprésente dans la nature. L’infection survient le plus souvent chez les animaux immunodéprimés. La plupart des chiens infectés présentent une diarrhée chronique du gros intestin, des lésions oculaires, des déficits neurologiques ou une combinaison de ces symptômes, mais divers tissus peuvent être affectés. Ce cas met en évidence une présentation unique de protothécose chez un chien, dans laquelle la boiterie résultant de l’ostéomyélite était le signe clinique prédominant.Message clinique clé :Bien que l’ostéomyélite soit une manifestation atypique, la protothécose peut être un diagnostic différentiel pour une lésion osseuse agressive et mérite d’être particulièrement prise en compte chez les chiens immunodéprimés.(Traduit par Dr Serge Messier).
Copyright and/or publishing rights held by the Canadian Veterinary Medical Association.
Figures
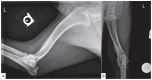
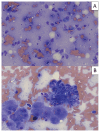
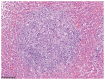
References
-
- Stenner VJ, Mackay B, King T, et al. Protothecosis in 17 Australian dogs and a review of the canine literature. Med Mycol. 2007;45:249–266. - PubMed
-
- Manino PM, Oliveira F, Ficken M, Swinford A, Burney D. Disseminated protothecosis associated with diskospondylitis in a dog. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2014;50:429–435. - PubMed
-
- Hollingsworth SR. Canine protothecosis. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2000;30:1091–1101. - PubMed
-
- Masuda M, Jagielski T, Danesi P, et al. Protothecosis in dogs and cats-new research directions. Mycopathologia. 2021;186:143–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
