Bioactive Glycyrrhizic Acid Ionic Liquid Self-Assembled Nanomicelles for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Anti-Photoaging Signal Peptides
- PMID: 39783908
- PMCID: PMC11848569
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202412581
Bioactive Glycyrrhizic Acid Ionic Liquid Self-Assembled Nanomicelles for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Anti-Photoaging Signal Peptides
Abstract
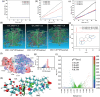
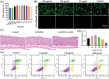
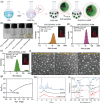
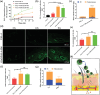
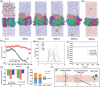
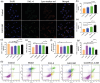
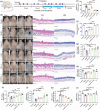
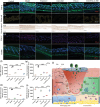
Sigal peptides have garnered remarkable efficacy in rejuvenating photoaged skin and delaying senescence. Nevertheless, their low solubility and poor permeability bring about a formidable challenge in their transdermal delivery. To address this challenge, bioactive ionic liquids (ILs) synthesized from natural glycyrrhizic acid (GA) and oxymatrine (OMT) with eminent biocompatibility is first prepared. The components ratios and inherent forming mechanisms of GA-OMT (GAO) are optimized by molecular dynamics simulations and density functional theory calculations. Remarkably, GAO can significantly improve the sparingly soluble properties of palmitoyl pentapeptide-4 (PAL-4), a model peptide drug. Subsequently, GAO self-assembled micelles loading PAL-4 (GAO/PAL-4-SM) are fabricated without additional auxiliary materials. The permeation and subcutaneous retention of PAL-4 are significantly promoted with 10wt.% GAO-SM. Moreover, GAO ILs facilitated PAL-4 permeation by enhancing its miscibility and interaction with stratum corneum (SC), offering a pulling effect and micellar structures for PAL-4, as elucidated by computational simulations. In cellular and animal photoaging experiments, GAO/PAL-4-SM possessed remarkable capabilities in boosting collagen and hyaluronic acid regeneration, mitigating inflammation and apoptosis, accelerating macrophage M2 polarization, thereby lessening skin wrinkles and leveraging elasticity. Collectively, the research innovatively designed an ILs self-assembled nano-micellar transdermal delivery system to enhance the permeability and anti-photoaging effect of signal peptides.
Keywords: computational simulations; glycyrrhizic acid; ionic liquid self‐assembled micelles; permeation enhancement; photoaging; signal peptides.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ionic liquids self-assembled micelles for transdermal delivery: characterization, functions and applications.Int J Pharm X. 2025 Jun 30;10:100350. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100350. eCollection 2025 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2025. PMID: 40688029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep eutectic solvent self-assembled reverse nanomicelles for transdermal delivery of sparingly soluble drugs.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 May 21;22(1):272. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02552-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38773580 Free PMC article.
-
Ionic liquid-iontophoresis mediates transdermal delivery of sparingly soluble drugs.Drug Deliv. 2025 Dec;32(1):2489730. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2025.2489730. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 40255114 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and evaluation of novel glycyrrhizic acid micelles for transdermal delivery of podophyllotoxin.Drug Deliv. 2016 Jun;23(5):1623-35. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2015.1135489. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26786787
-
Recent Developments in Ionic Liquid-Assisted Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery.Pharm Res. 2022 Oct;39(10):2335-2351. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03322-x. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 35773446 Review.
Cited by
-
Co-assembled Glycyrrhiza nanoparticles embedded supramolecular protein hydrogels to enhance licochalcone A release for acute inflammation management.Int J Pharm X. 2025 May 30;9:100343. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100343. eCollection 2025 Jun. Int J Pharm X. 2025. PMID: 40521161 Free PMC article.
-
Ionic liquids self-assembled micelles for transdermal delivery: characterization, functions and applications.Int J Pharm X. 2025 Jun 30;10:100350. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100350. eCollection 2025 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2025. PMID: 40688029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
