Nonselective β-Adrenergic Receptor Inhibitors Impair Hematopoietic Regeneration in Mice and Humans after Hematopoietic Cell Transplants
- PMID: 39786370
- PMCID: PMC11962394
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0719
Nonselective β-Adrenergic Receptor Inhibitors Impair Hematopoietic Regeneration in Mice and Humans after Hematopoietic Cell Transplants
Abstract
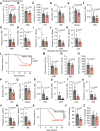
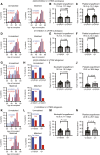
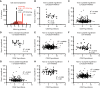
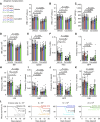
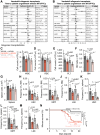
Peripheral nerves promote mouse bone marrow regeneration by activating β2- and β3-adrenergic receptor signaling, raising the possibility that nonselective β-blockers could inhibit engraftment after hematopoietic cell transplants (HCT). We observed no effect of β-blockers on steady-state mouse hematopoiesis. However, mice treated with a nonselective β-blocker (carvedilol), but not a β1-selective inhibitor (metoprolol), exhibited impaired hematopoietic regeneration after syngeneic or allogeneic HCTs. At two institutions, patients who received nonselective, but not β1-selective, β-blockers after allogeneic HCT exhibited delayed platelet engraftment and reduced survival. This was particularly observed in patients who received posttransplant chemotherapy for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis, which also accentuated the inhibitory effect of carvedilol on engraftment in mice. In patients who received autologous HCTs, nonselective β-blockers were associated with little or no delay in engraftment. The inhibitory effect of nonselective β-blockers after allogeneic HCT was overcome by transplanting larger doses of hematopoietic cells. Significance: Patients who receive allogeneic HCTs followed by posttransplant chemotherapy for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis may be at risk of delayed engraftment and increased mortality if administered nonselective β-blockers after transplantation. Transient discontinuation of nonselective β-blockers or transitioning to β1-selective inhibitors after HCT may accelerate engraftment and improve clinical outcomes. See related commentary by Bhatia, p. 666.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Kishtagari reports personal fees from Servier Pharmaceuticals, Incyte, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Sobi, MorphoSys/Novartis, Geron, and Syndax outside the submitted work. C.M. Blackman reports personal fees from Jazz Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. A.M. Zeidan reports personal fees from the following sources outside the submitted work; research funding (institutional) from Celgene/BMS, AbbVie, Astex, Pfizer, Kura, MedImmune/AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Takeda, Novartis, Shattuck Labs, Geron, Foran, and APREA; participating in advisory boards of, being a consultant with, and receiving honoraria from AbbVie, Pfizer, Celgene/BMS, Jazz, Incyte, Agios, Servier, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, Geron, Taiho, Seattle Genetics, Otsuka, BeyondSpring, Takeda, Isis Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, Janssen, Genentech, Epizyme, Syndax, Gilead, Kura, Chiesi, ALX Oncology, BioCryst, Notable, Orum, Mendus, Zentalis, Schrödinger, Regeneron, Syros, and Tyme; as well as serving on the clinical trial committees for Novartis, AbbVie, Gilead, Syros, BioCryst, ALX Oncology, Kura Oncology, Geron, and Celgene/BMS. Y.F. Madanat reports personal fees from BMS, Kura Oncology, Blueprint Medicines, Geron, Curio Science, Stemline Therapeutics, Taiho Oncology, Sobi, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Cogent Biosciences, and AbbVie, as well as nonfinancial support from MD Education outside the submitted work. S.J. Morrison reports grants from the NIH, Josephine Hughes Sterling Foundation, Kleberg Foundation, Moody Medical Research Institute, NCI, Department of Defense, HHMI, and Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas during the conduct of the study; personal fees and nonfinancial support from Garuda Therapeutics and Kojin Therapeutics; as well as personal fees from Inception Therapeutics outside the submitted work. S.S. Chung reports grants from the NIH, Department of Defense, and the Edward P. Evans Foundation during the conduct of the study. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures


References
-
- Katayama Y, Battista M, Kao WM, Hidalgo A, Peired AJ, Thomas SA, et al. Signals from the sympathetic nervous system regulate hematopoietic stem cell egress from bone marrow. Cell 2006;124:407–21. - PubMed
-
- Tikhonova AN, Aifantis I. Pain-sensing neurons mobilize blood stem cells from bone marrow. Nature 2021;589:520–1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

