Odronextamab monotherapy in R/R DLBCL after progression with CAR T-cell therapy: primary analysis of the ELM-1 study
- PMID: 39786390
- PMCID: PMC12002204
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2024027044
Odronextamab monotherapy in R/R DLBCL after progression with CAR T-cell therapy: primary analysis of the ELM-1 study
Abstract
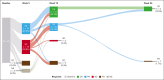
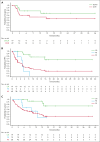
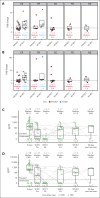
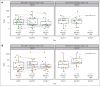
Patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma progressing after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy have dismal outcomes. The prespecified post-CAR-T expansion cohort of the ELM-1 study investigated the efficacy and safety of odronextamab, a CD20×CD3 bispecific antibody, in patients with disease progression after CAR-Ts. Sixty patients received IV odronextamab weekly for 4 cycles followed by maintenance until progression. The primary end point was objective response rate (ORR) by independent central review. The median number of prior lines of therapy was 3 (range, 2-9), 71.7% were refractory to CAR-Ts, and 48.3% relapsed within 90 days of CAR-T therapy. After a median follow-up of 16.2 months, ORR and complete response (CR) rate were 48.3% and 31.7%, respectively. Responses were similar across prior CAR-T products and time to relapse on CAR-T therapy. Median duration of response was 14.8 months and median duration of CR was not reached. Median progression-free survival and overall survival were 4.8 and 10.2 months, respectively. The most common treatment-emergent adverse event was cytokine release syndrome (48.3%; no grade ≥3 events). No cases of immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome were reported. Grade ≥3 infections occurred in 12 patients (20.0%), 2 of which were COVID-19. Odronextamab monotherapy demonstrated encouraging efficacy and generally manageable safety, supporting its potential as an off-the-shelf option for patients after CAR-T therapy. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02290951.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.S.T. reports consultancy for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Genmab, Incyte, Janssen, and Kite; and research funding from AstraZeneca, Kite, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Roche. M.M. reports consultancy for Bayer, Genentech, GM Biosciences, Johnson & Johnson, Pharmacyclics, Roche, and Seattle Genetics; research funding from Bayer, Genentech, GM Biosciences, ImmunoVaccine Technologies, Johnson & Johnson, Pharmacyclics, Roche, and Seattle Genetics; honoraria from ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Epizyme, Genentech, IMV Therapeutics, Johnson & Johnson, Kite, Pharmacyclics, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Roche, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, and Takeda; and membership on an entity’s board of directors or advisory committees for Allogene, Genentech, Genmab, and Merck. J.N.A. reports consultancy for AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Genentech, Janssen, Eli Lilly, NeoGenomics, and Pharmacyclics; and research funding from BeiGene, Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, and Janssen. S.M.A. reports trial research funding from ADC Therapeutics, Affimed, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Takeda. J.E.A. reports speaker’s fee from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. J.-M.M. reports consultancy for Ideogen, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead, Merck, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Therakos/Mallinckrodt; research funding from Astex Pharmaceuticals; and travel support from Beigene, Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. S.M.O. reports consultancy for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Autolus, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen Oncology, Johnson & Johnson, Loxo Oncology, Merck, Pfizer, and Pharmacyclics; and research funding from Alliance, Caribou Biosciences, Nurix Therapeutics, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Y.C., D.M.F., M.Z., J.B.-V., A.C., H.M., and S.A. hold stock or stock options for, and are employees of, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. J.L.C. reports consultancy for Genmab, Incyte, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Kite Pharma, MorphoSys, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Seagen; funding from AbbVie, Bayer, Genentech/Roche, and Merck; and employment with the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Two strikes, base hit: odronextamab after CAR T cells in LBCL.Blood. 2025 Apr 3;145(14):1441-1442. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024027961. Blood. 2025. PMID: 40178849 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45–56. - PubMed
-
- Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396(10254):839–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

